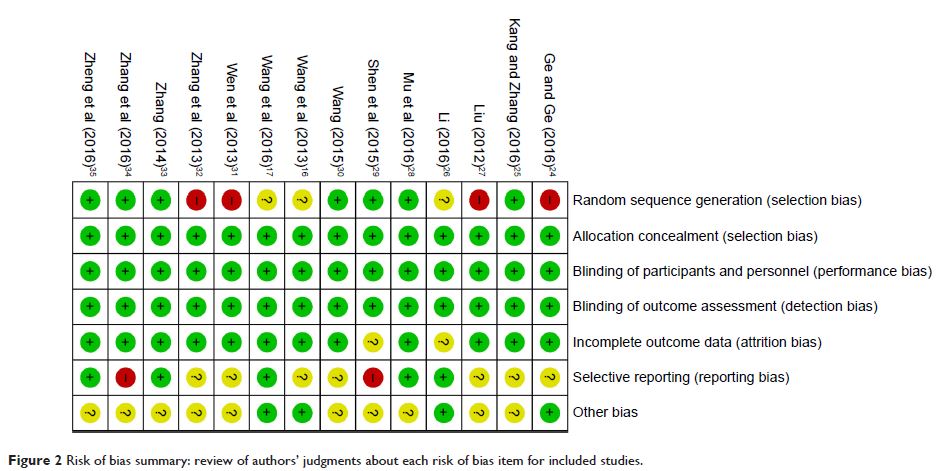
111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
由树突细胞 - 细胞因子诱导、杀伤细胞介导的胰腺癌免疫治疗的临床应用: 最新的荟萃分析
Authors Zhang YC, Zhang X, Zhang AQ, Li K, Qu K
Received 7 June 2017
Accepted for publication 4 August 2017
Published 23 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4173—4192
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143382
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Purpose: This study
aimed to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of dendritic
cells–cytokine-induced killer (DC–CIK) cells immunotherapy in treating
pancreatic cancer (PC) patients.
Methods: Data were collected from published articles of clinical trials. Databases including Web of Science, EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Wanfang, and CNKI were searched. The main outcome measures in this research included the overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS), patients’ quality of life (QoL), immune function, and adverse events. Comparative analysis was conducted between DC–CIK immunotherapy and chemotherapy (combined therapy) and chemotherapy alone.
Results: This analysis covered 14 trials with 1,088 PC patients involved. The combined therapy showed advantages over chemotherapy alone in ORR (odds ratio [OR] =1.69, 95% confidence interval [CI] =1.20–2.38, P =0.003), DCR (OR =2.33, 95% CI =1.63–3.33, P <0.00001), OS (1-year OS, OR =3.61, 95% CI =2.41–5.40, P <0.00001; 3-year OS, OR =2.65, 95% CI =1.56–4.50, P =0.0003) and patients’ QoL (P <0.01) with statistical significance. After immunotherapy, lymphocyte subsets’ percentages of CD3+ (P <0.00001), CD4+ (P =0.01), CD3+CD56+ (P <0.00001), and cytokine levels of IFN-γ (P <0.00001) were significantly increased, and the percentages of CD4+CD25+CD127low (P <0.00001) and levels of IL-4 (P <0.0001) were significantly decreased, whereas analysis on CD8+ (P =0.59) and CD4+/CD8+ ratio (P =0.64) did not show a significant difference.
Conclusion: The combination of DC–CIK immunotherapy and chemotherapy is effective for PC treatment, indicated by prolonging the PC patients’ survival time, which benefit from reconstructed immune function of patients.
Keywords: cytokine-induced killer cells, dendritic cells, pancreatic cancer, immunotherapy, meta-analysis
Methods: Data were collected from published articles of clinical trials. Databases including Web of Science, EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Wanfang, and CNKI were searched. The main outcome measures in this research included the overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), overall survival (OS), patients’ quality of life (QoL), immune function, and adverse events. Comparative analysis was conducted between DC–CIK immunotherapy and chemotherapy (combined therapy) and chemotherapy alone.
Results: This analysis covered 14 trials with 1,088 PC patients involved. The combined therapy showed advantages over chemotherapy alone in ORR (odds ratio [OR] =1.69, 95% confidence interval [CI] =1.20–2.38, P =0.003), DCR (OR =2.33, 95% CI =1.63–3.33, P <0.00001), OS (1-year OS, OR =3.61, 95% CI =2.41–5.40, P <0.00001; 3-year OS, OR =2.65, 95% CI =1.56–4.50, P =0.0003) and patients’ QoL (P <0.01) with statistical significance. After immunotherapy, lymphocyte subsets’ percentages of CD3+ (P <0.00001), CD4+ (P =0.01), CD3+CD56+ (P <0.00001), and cytokine levels of IFN-γ (P <0.00001) were significantly increased, and the percentages of CD4+CD25+CD127low (P <0.00001) and levels of IL-4 (P <0.0001) were significantly decreased, whereas analysis on CD8+ (P =0.59) and CD4+/CD8+ ratio (P =0.64) did not show a significant difference.
Conclusion: The combination of DC–CIK immunotherapy and chemotherapy is effective for PC treatment, indicated by prolonging the PC patients’ survival time, which benefit from reconstructed immune function of patients.
Keywords: cytokine-induced killer cells, dendritic cells, pancreatic cancer, immunotherapy, meta-analysis