111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

EpCAM 适体官能化的聚多巴胺 (dopamine) 涂层的介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子用于结肠直肠癌靶向治疗
Authors Li Y, Duo Y, Bao SY, He L, Ling K, Luo J, Zhang Y, Huang H, Zhang H, Yu X
Received 6 June 2017
Accepted for publication 26 July 2017
Published 26 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6239—6257
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S143293
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
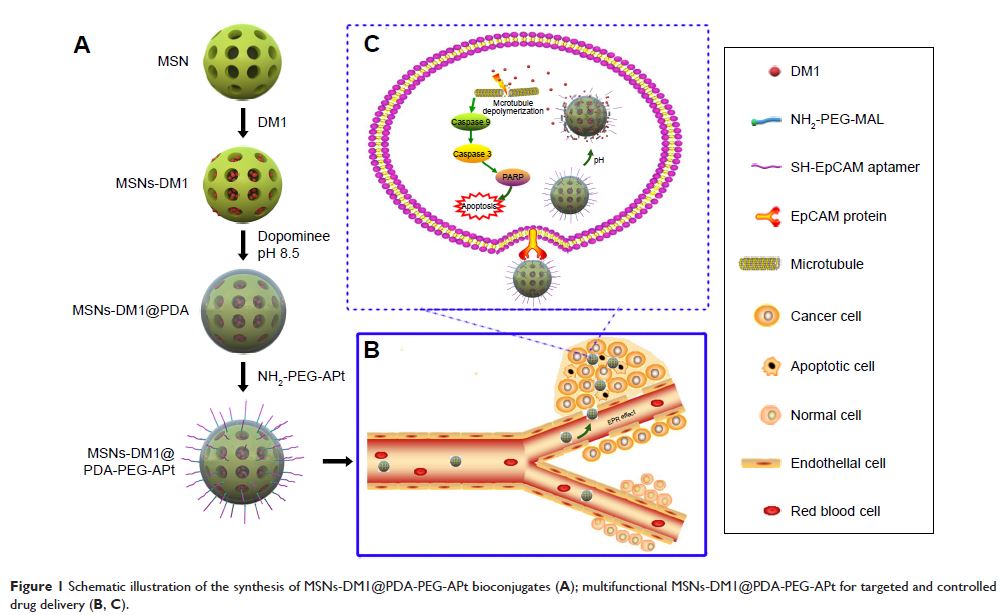
Abstract: DM1, a maytansine derivative,
is a highly potential cytotoxic agent but with severe side effects; therefore,
its application in clinical cancer therapy is limited. Here, in order to
mitigate this intrinsic drawback of DM1, we developed mesoporous silica
nanoparticles (MSNs) loaded with DM1 and surface-decorated with hydrochloride
dopamine (PDA), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and epithelial cell adhesion
molecule (EpCAM) aptamer (APt) for the targeted treatment of colorectal cancer
(CRC). In this system, the PDA coating could be used as pH-sensitive
gatekeepers to control the release of DM1 from MSNs in response to the pH
stimulus and EpCAM APt-guided active targeting enables the increased delivery
of DM1 to CRC as well as a reduction in toxicity and side effects by minimizing
the exposure of normal tissues to DM1. Results demonstrated that DM1 inhibited
the formation of microtubules and induced apoptosis in tumor cells via caspase
signaling. In comparison with the control groups, the MSNs-DM1@PDA-PEG-APt
bioconjugates exhibited increased binding ability and much higher cytotoxicity
to the CRC SW480 cell line. Furthermore, in vivo assays confirmed the
advantages of such a strategy. These findings suggested that
MSNs-DM1@PDA-PEG-APt could represent a promising therapeutic platform for
EpCAM-positive CRC.
Keywords: DM1, EpCAM
aptamer, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, colorectal cancer