111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA 在人类肿瘤肝癌中高度上调的研究进展
Authors Ma Z, Huang H, Xu Y, He X, Wang J, Hui B, Ji H, Zhou J, Wang K
Received 13 March 2017
Accepted for publication 2 May 2017
Published 25 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4711—4717
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S136915
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Abstract: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a group of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) >200
nucleotides in length that govern diverse biological processes. Recent evidence
suggests that lncRNAs are involved in cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis,
invasion, migration, and metastasis. Dysregulation of lncRNAs has been observed
in various tumors, and lncRNAs act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in these
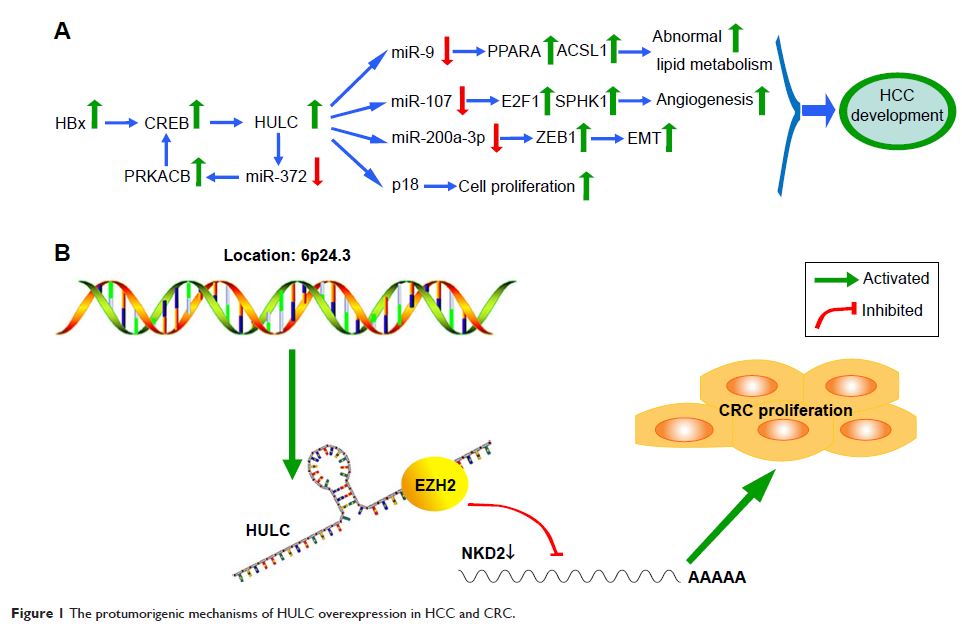
malignancies. It has been revealed that lncRNA highly upregulated in liver
cancer (HULC) is tightly correlated with a number of cancers such as
hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, osteosarcoma, and
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Depletion of HULC suppressed cancer cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion and induced apoptosis. Additionally,
HULC may function as a diagnostic biomarker and prognostic indicator for some
tumors. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the role of HULC
in cancer progression and the clinical management of human cancers.
Keywords: lncRNA, HULC,
cancer