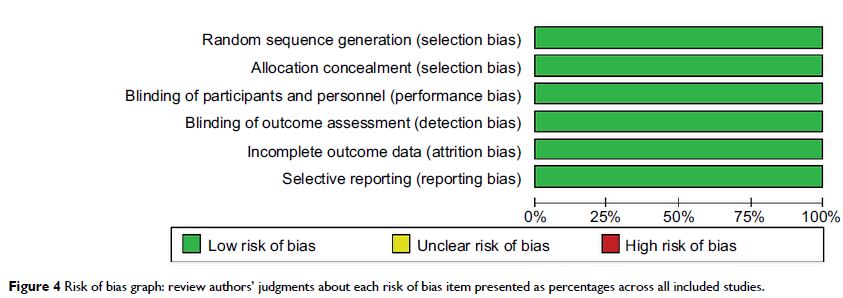
111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Spotlight on eluxadoline for the treatment of patients with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea
Authors Fragkos KC
Received 29 May 2017
Accepted for publication 10 September 2017
Published 25 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 229—240
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S123621
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wing-Kin Syn
Background: Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) has limited options
for treatment currently, including mainly anti-motility medications,
antispasmodics, and antidepressants. This review discusses the properties of a
new drug, eluxadoline, a gut-targeting mu- and kappa-opioid receptor agonist
and a delta-opioid receptor antagonist, and its efficacy and safety in patients
with IBS-D.
Materials and methods: A systematic review of the literature was undertaken
to identify studies that had investigated eluxadoline as a treatment in IBS-D.
A narrative review of other information is provided with respect to
pharmacological and chemical properties. Where suitable, meta-analysis was
performed with a random-effects model to produce a pooled estimate.
Results: Eluxadoline showed efficacy improving stool
consistency (standardized mean difference [SMD]: -0.29 at 12 weeks, p = 0.0004; -0.46 at
26 weeks, p = 0.0001),
global symptoms (SMD: -0.15 at 12 weeks, p =
0.006; -0.14 at 26 weeks, p = 0.02),
quality of life (SMD: 0.21 at 12 weeks, p <
0.0001; 0.16 at 26 weeks, p = 0.007),
pain (SMD: -0.17 at 12 weeks, p = 0.001;
-0.16 at 26 weeks, p = 0.01), and
adequate relief (odds ratio [OR]: 1.99 at 12 weeks, p < 0.00001; 1.78 at
26 weeks, p <
0.0001). It also improved IBS severity and other abdominal symptoms such as
bloating, discomfort, and risk of urgency and fecal incontinence. Its main side
effects included constipation (OR: 3.49, p <
0.00001), vomiting (OR: 3.42, p = 0.0002),
abdominal pain (OR: 1.78, p = 0.007), and
nausea (OR: 1.42, p = 0.07). The
overall quality of trials was satisfactory with the meta-analyses providing
largely homogeneous outcomes.
Conclusion: Eluxadoline’s place in clinical practice might
prove useful since the pharmacological options of IBS-D are limited and
eluxadoline showed a positive effect in treating the symptoms of IBS-D.
Keywords: eluxadoline,
irritable bowel syndrome, diarrhea, stool consistency, pain