111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过 12 周鼻内布地奈德 (Budesonide) 治疗减少行腺样体切除术的频率
Authors Hong H, Chen F, Zheng X, Liao W, Liao Z, Cao Y, He H, Zhu Z, Fan Y
Received 22 June 2017
Accepted for publication 7 August 2017
Published 3 October 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1309—1316
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S144659
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: There is little evidence on the role of topical budesonide in
reducing the frequency of adenoidectomy, although it was reported that topical
budesonide can effectively ameliorate the symptoms of adenoid hypertrophy (AH).
This study was aimed to investigate the possibility and safety of alternatives
to adenoidectomy with a 12-week treatment with nasal budesonide.
Materials and methods: One hundred patients with AH were randomized to
receive either a double-blind budesonide (1 mg once daily) or placebo treatment
for 2 weeks by transnasal nebulization. A further 12-week open study,
budesonide spray (64 µg per nostril at bedtime) was administered to the
treatment group. During the final 12 weeks of follow-up, the frequency of
adenotonsillectomy, side effects, the degree of nasal obstruction, nasal
discharge, and snoring were assessed.
Results: Out of the 100 total enrolled patients, 92 children
with AH completed the study. After the 2-week treatment with transnasal
budesonide nebulization, the symptoms of AH significantly decreased compared to
the control group. Responders (n=26) who had initially improved showed
significantly decreased symptoms of AH, and the frequency of adenotonsillectomy
during the follow-up (14 and 26 weeks) was compared with that of the control
group and non-responders (n=21) who did not respond to the initial 2-week
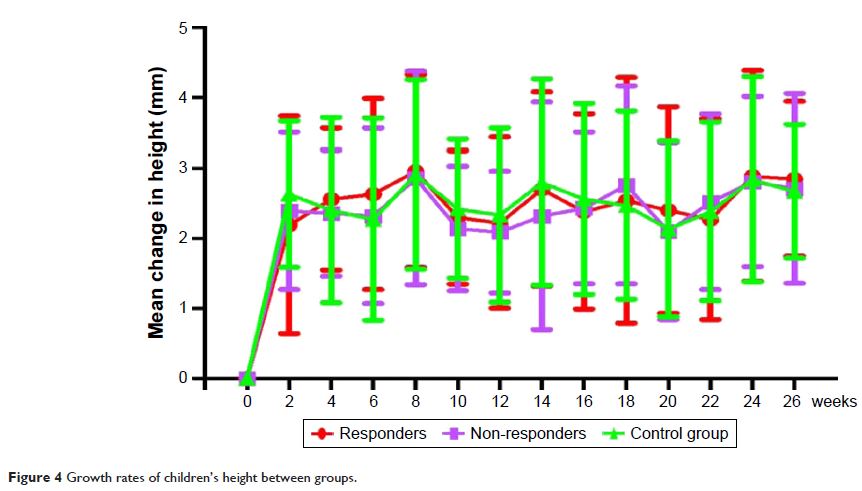
budesonide therapy. The 12-week nasal budesonide treatment did not suppress the
growth rate of children’s height or cause other side effects.
Conclusion: AH children who had improved after an initial
2-week budesonide therapy can achieve clinical improvements and decreased
frequency of adenoidectomy following the therapy with a 12-week treatment with
nasal budesonide.
Keywords: adenoid
hypertrophy, adenoidectomy, budesonide, frequency, treatment