111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in COPD: from bench to bedside
Authors Antunes MA, Lapa e Silva JR, Rocco PRM
Received 18 July 2017
Accepted for publication 8 September 2017
Published 16 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3017—3027
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S146671
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Abstract: COPD
is the most frequent chronic respiratory disease and a leading cause of
morbidity and mortality. The major risk factor for COPD development is
cigarette smoke, and the most efficient treatment for COPD is smoking
cessation. However, even after smoking cessation, inflammation, apoptosis, and
oxidative stress may persist and continue contributing to disease progression.
Although current therapies for COPD (primarily based on anti-inflammatory agents)
contribute to the reduction of airway obstruction and minimize COPD
exacerbations, none can avoid disease progression or reduce mortality. Within
this context, recent advances in mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) therapy have
made this approach a strong candidate for clinical use in the treatment of
several pulmonary diseases. MSCs can be readily harvested from diverse tissues
and expanded with high efficiency, and have strong immunosuppressive
properties. Preclinical studies have demonstrated encouraging outcomes of MSCs
therapy for lung disorders, including emphysema. These findings instigated
research groups to assess the impact of MSCs in human COPD/emphysema, but
clinical results have fallen short of expectations. However, MSCs have
demonstrated a good adjuvant role in the clinical scenario. Trials that used
MSCs combined with another, primary treatment (eg, endobronchial valves) found
that patients derived greater benefit in pulmonary function tests and/or
quality of life reports, as well as reductions in systemic markers of
inflammation. The present review summarizes and describes the more recent
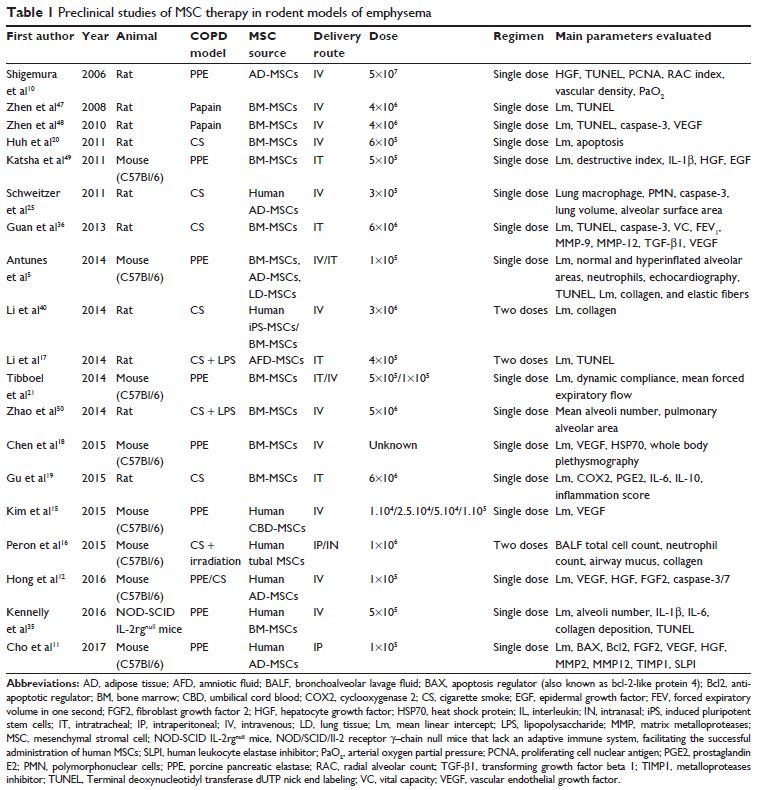
preclinical studies that have been published about MSC therapy for
COPD/emphysema and discusses what has already been applied about MSCs treatment
in COPD patients in the clinical setting.
Keywords: emphysema, mesenchymal stromal cells, inflammation, remodeling, repair