111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

多功能金纳米棒和多西紫杉醇封装脂质体用于热疗与化疗联合治疗
Authors Hua H, Zhang N, Liu D, Song L, Liu T, Li S, Zhao Y
Received 14 June 2017
Accepted for publication 17 September 2017
Published 25 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7869—7884
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S143977
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Personalized and precise nanomedicines are highly demanded for
today’s medical needs. Liposomes are ideal candidates for the construction of
multifunctional drug delivery systems. In this study, a liposome was used to
improve the clinical issues of docetaxel (Doc), a potent antimitotic
chemotherapy for prostate cancer (PC). RLT, a low-density lipoprotein receptor
(LDLR)-binding peptide, and PEG were conjugated to the liposomes, and gold
nanorods (GNRs) were also incorporated into the liposomes. The
GNRs/Doc-liposome-RLT (GNRs/DocL-R) was tested in PC-3 cells and in PC-3
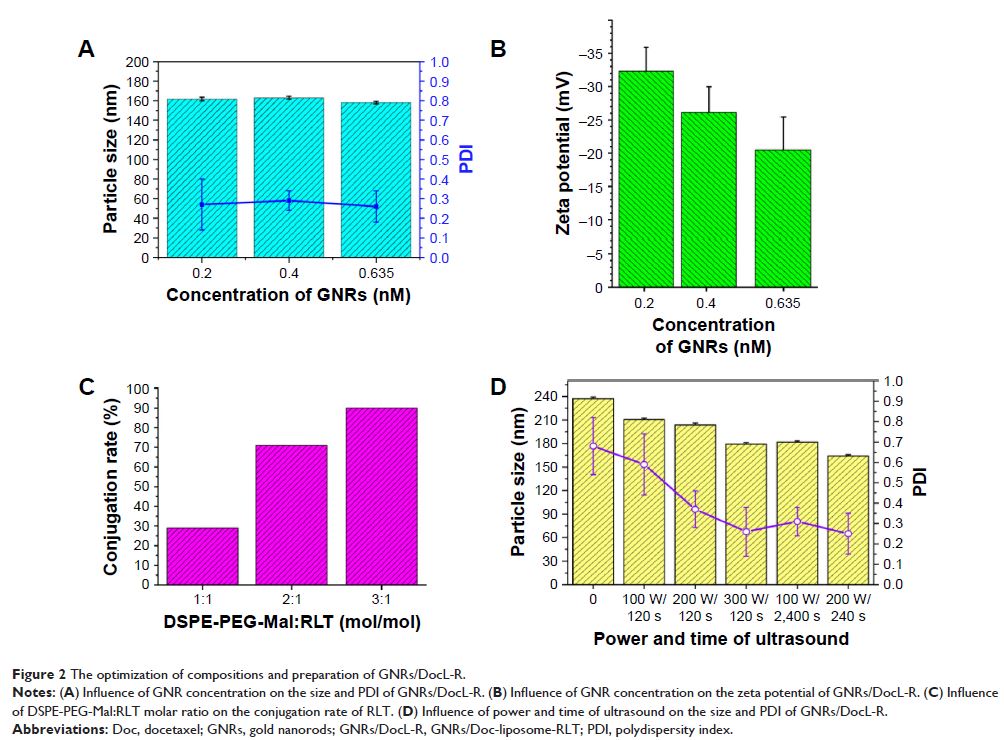
tumor-bearing nude mice. Results showed that GNRs/DocL-R possessed a diameter
approximately 163.15±1.83 nm and a zeta potential approximately
-32.8±2.16 mV. GNRs/DocL-R showed enhanced intracellular entrance,
increased accumulation in the implanted tumor region, and the highest tumor
inhibition in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the multifunctional GNRs/DocL-R was
a potential cancer treatment via combined chemo- and thermotherapy.
Keywords: gold nanorods,
docetaxel, liposomes, prostate cancer, LDL receptor targeting