111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

5-氮杂-2'-脱氧胞苷通过抑制 p16Ink4a 在肺组织中的表达保护小鼠避免患上肺气肿
Authors He ZH, Chen Y, Chen P, He SD, Zeng HH, Ye JR, Liu D, Cao J
Received 26 December 2016
Accepted for publication 24 July 2017
Published 30 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3149—3158
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S131090
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Charles Downs
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: There
is a growing realization that COPD, or at least emphysema, involves several
processes presenting in aging and cellular senescence. Endothelial progenitor
cells (EPCs) contribute to neovascularization and play an important role in the
development of COPD. The gene for p16Ink4a is a
major dominant senescence one. The aim of the present study was to observe
changes in lung function, histomorphology of lung tissue, and expression of p16Ink4a in lung tissue and bone marrow-derived
EPCs in emphysematous mice induced by cigarette-smoke extract (CSE), and
further to search for a potential candidate agent protecting against emphysema
induced by CSE.
Materials and
methods: An animal emphysema model was
induced by intraperitoneal injection of CSE. 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-CdR)
was administered to the emphysematous mice. Lung function and histomorphology
of lung tissue were measured. The p16Ink4a protein
and mRNA in EPCs and lung tissues were detected using Western blotting and
quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, respectively.
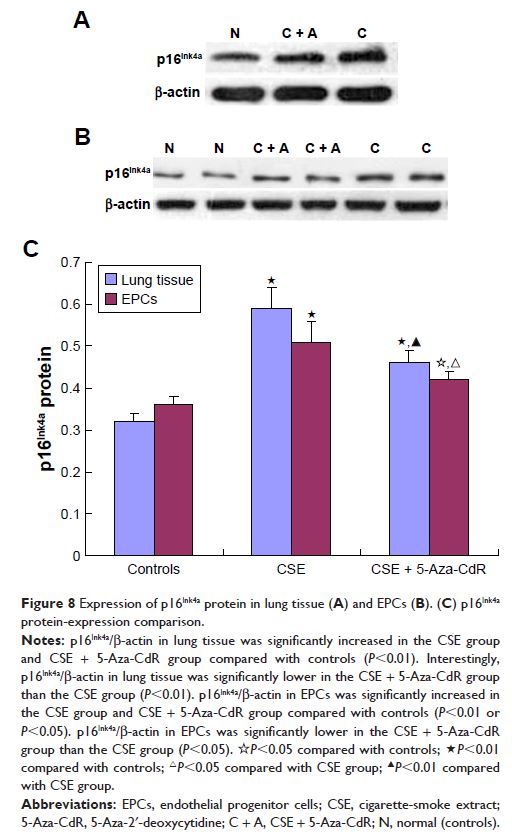
Results: CSE induced emphysema with increased p16Ink4a expression in lung tissue and bone
marrow-derived EPCs. 5-Aza-CdR partly protected against emphysema, especially
in the lung-morphology profile, and partly protest against the overexpression
of p16Ink4a in EPCs and lung tissue induced by CSE.
Conclusion: 5-Aza-CdR partly protected against emphysema in mice via
suppressing p16Ink4a expression in EPCs and lung
tissue.
Keywords: 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine, cigarette smoke, emphysema, endothelial
progenitor cells, p16Ink4a