111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

开发和验证由五种蛋白质组成的血液生物标记物用于结肠直肠癌的早期检测
Authors Chen H, Qian J, Werner S, Cuk K, Knebel P, Brenner H
Received 16 June 2017
Accepted for publication 30 August 2017
Published 31 October 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 517—526
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S144171
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Henrik Toft Sorensen
Objective: Reliable
noninvasive biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer (CRC) are
highly desirable for efficient population-based screening with high adherence
rates. We aimed to discover and validate blood-based protein markers for the
early detection of CRC.
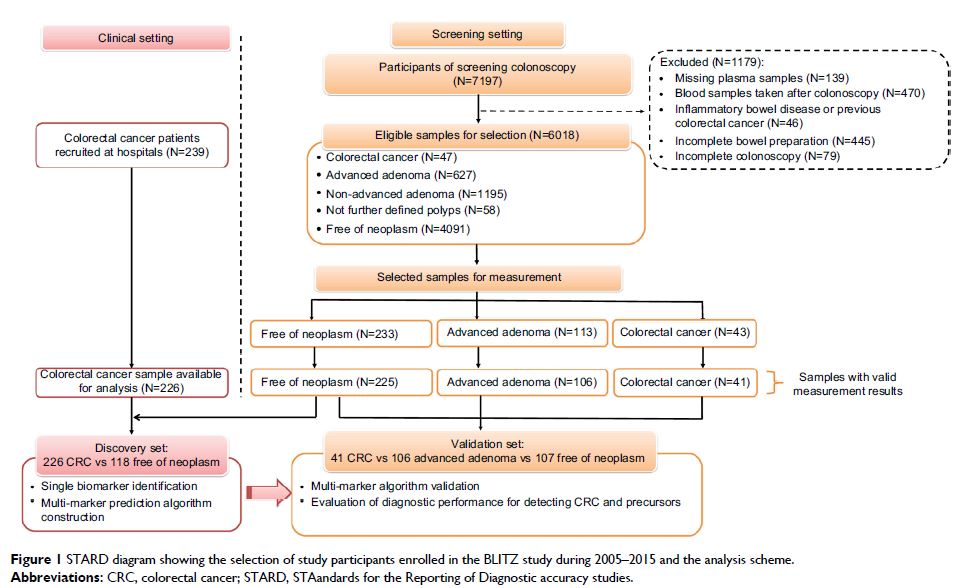
Patients and
methods: A two-stage design with a
discovery and a validation set was used. In the discovery phase, plasma levels
of 92 protein markers and serum levels of TP53 autoantibody were measured in 226
clinically recruited CRC patients and 118 controls who were free of colorectal
neoplasms at screening colonoscopy. An algorithm predicting the presence of CRC
was derived by Lasso regression and validated in a validation set consisting of
all available 41 patients with CRC and a representative sample of 106
participants with advanced adenomas and 107 controls free of neoplasm from a
large screening colonoscopy cohort (N=6018). Receiver operating characteristic
(ROC) analyses were conducted to evaluate the diagnostic performance of
individual biomarkers and biomarker combinations.
Results: An algorithm based on growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15),
amphiregulin (AREG), Fas antigen ligand (FasL), Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3
ligand (Flt3L) and TP53 autoantibody was constructed. In the validation set,
the areas under the curves of this five-marker algorithm were 0.82 (95% CI,
0.74–0.90) for detecting CRC and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.52–0.69) for detecting
advanced adenomas. At cutoffs yielding 90% specificity, the sensitivities (95%
CI) for detecting CRC and advanced adenomas were 56.4% (38.4%–71.8%) and 22.0%
(13.4%–35.4%), respectively. The five-marker panel showed similar diagnostic
efficacy for the detection of early- and late-stage CRC.
Conclusion: The identified most promising biomarkers could contribute to the
development of powerful blood-based tests for CRC screening in the future.
Keywords: amphiregulin, growth differentiation factor 15, adenoma,
colorectal cancer, screening