111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

东亚慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者的肺功能和使用噻托溴铵/奥达特罗的长期安全性
Authors Bai C, Ichinose M, Lee SH, Lee KH, Jöns O, Bothner U, Zhao Y, Buhl R
Received 23 March 2017
Accepted for publication 13 July 2017
Published 20 November 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3329—3339
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S137719
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Hsiao-Chi Chuang
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background and
purpose: While the efficacy and safety
of combined tiotropium and olodaterol in patients with COPD was established in
a large clinical trial program, it is important to assess whether clinical data
can be applied to geographic patient groups, particularly for East Asian
patients who may have a different phenotypic profile to the global trial
population. This study aimed to compare the lung function and safety profiles
of tiotropium/olodaterol and monocomponents in East Asian and global
populations from the TONADO® trials.
Materials and methods: In the replicate, double-blind, parallel-group,
active-controlled, randomized, 52-week, Phase III TONADO studies, patients
received tiotropium/olodaterol, tiotropium, or olodaterol. We assessed the
forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) area under the
curve from 0 to 3 hours (AUC0–3) response and
trough FEV1 response at 24 weeks for the approved
doses, tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 µg, tiotropium 5 µg, and olodaterol 5 µg.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were recorded throughout treatment and ≤21
days after study medication.
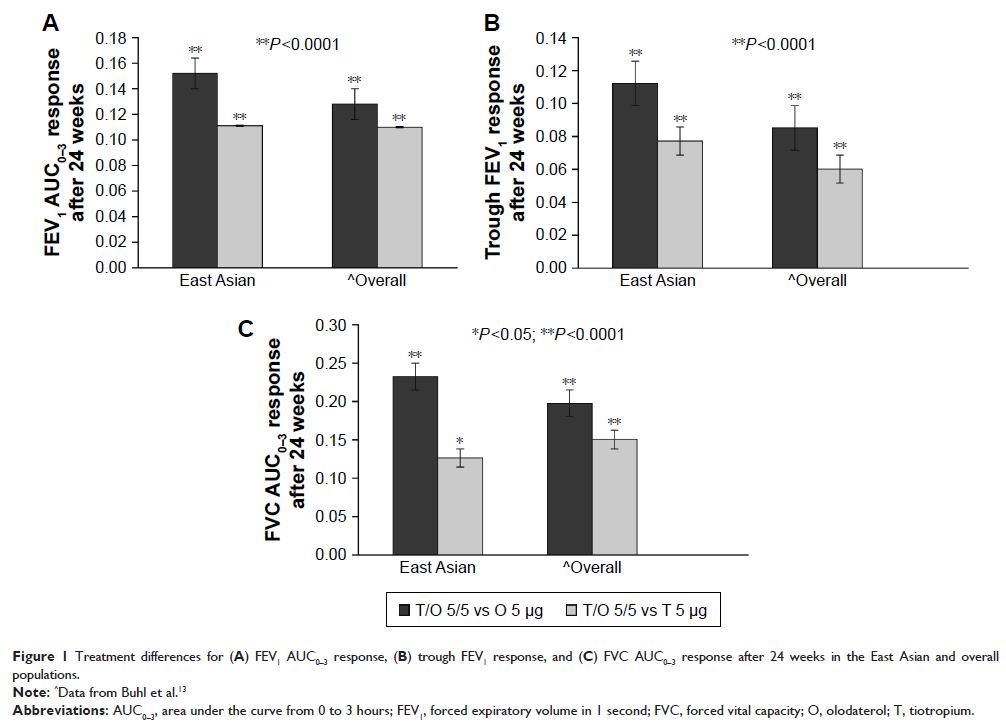
Results: In the East Asian population, 1,152 patients were
randomized (5,163 overall). After 24 weeks, FEV1 AUC0–3 and
trough FEV1 responses were greater (P <0.0001) with
tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 µg in both populations versus tiotropium or
olodaterol. The East Asian population showed slightly greater trough FEV1 treatment differences between
tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 µg and tiotropium compared to the overall
population. Generally, no increase in adverse events was seen with
tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 µg compared to tiotropium and olodaterol in either
population.
Conclusion: The efficacy and safety profile of
tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 µg has been demonstrated for both East Asian and
global populations.
Keywords: COPD, adverse
effects, pulmonary function, TONADO®