111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-34a 表达在甲状腺疾病中的临床意义:一项关于 18F-FDG PET-CT 的研究
Authors Chen L, Yang C, Feng J, Liu X, Tian Y, Zhao L, Xie R, Liu C, Zhao S, Sun H
Received 2 June 2017
Accepted for publication 14 November 2017
Published 15 December 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 903—913
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S143110
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: To evaluate the possible roles of miR-34a expression in thyroid
lesions, to unravel the correlation between fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake and
miR-34a expression and moreover, to discover the underlying mechanisms by which
miR-34a regulates FDG avidity.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 75 patients with pathology-confirmed
thyroid diseases who underwent 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) within 3
months before undergoing thyroid surgery and miR-34a analysis from June 2012 to
July 2017. 18F-FDG uptake of thyroid
lesions was also analyzed semiquantitatively using maximum standardized uptake
value (SUVmax). The association between miR-34a expression and
clinicopathological variables (age, sex, TNM stage, histopathology, lesion
numbers, location and 18F-FDG avidity) was investigated. When there were multiple lesions in
thyroid bed, only the one with the highest 18F-FDG uptake was analyzed. Next, we inhibited the miR-34a expression in
TPC-1 cells and detected the expression of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) mRNA
and protein.
Results: In the patients cohort, miR-34a was upregulated in those with
malignant thyroid diseases compared with benign lesions. The expression of
miR-34a was associated with tumor stages, histopathological types and SUVmax.
There was an inverse relationship between miR-34a expression and SUVmax in
patients with thyroid diseases (Spearman correlation coefficient =
–0.553, P < 0.0001). With an
SUVmax of 4.3 as the threshold, sensitivity and specificity of the prediction
of miR-34a expression (low or high) were 70% and 94.3%, respectively. The area
under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.843 (95% confidence
interval: 0.749, 0.936; P = 0.001).
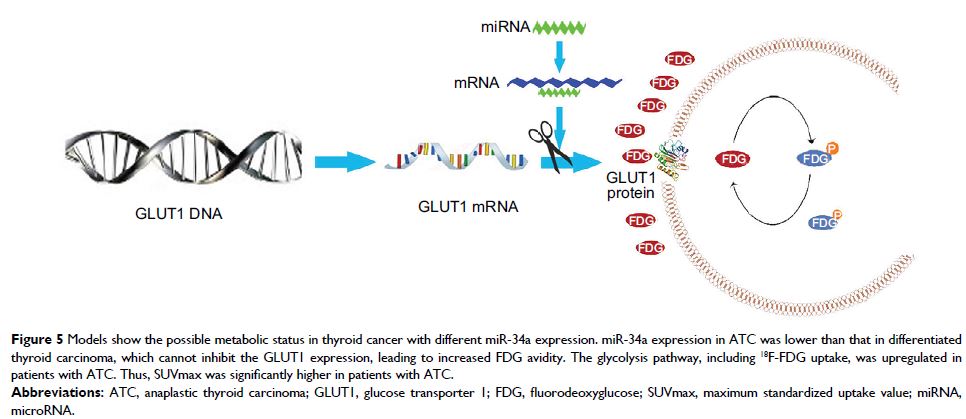
Inhibiting miR-34a in TPC-1 cells significantly increased GLUT1 mRNA and
protein expression.
Conclusion: miR-34a expression was upregulated in thyroid lesions, negatively
correlated with SUVmax and can be predicted by FDG SUVmax. In addition, miR-34a
may regulate FDG avidity via targeting GLUT1.
Keywords: miR-34a, thyroid cancer, PET/CT