111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HSPs 在人类胃肠癌中的预后作用:一项系统回顾和荟萃分析
Authors Ge H, Yan Y, Guo L, Tian F, Wu D
Received 1 November 2017
Accepted for publication 6 December 2017
Published 15 January 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 351—359
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S155816
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: Heat shock proteins
(HSPs) have been reported to be overexpressed in a wide range of human tumors.
It has been shown that HSPs act as an oncogenic regulator and are involved in
tumorigenesis. The clinical and prognostic significance of HSPs in
gastrointestinal cancers (GICs) remains controversial. The aim of this study
was to conduct a meta-analysis to assess the prognostic value of HSPs in GICs.
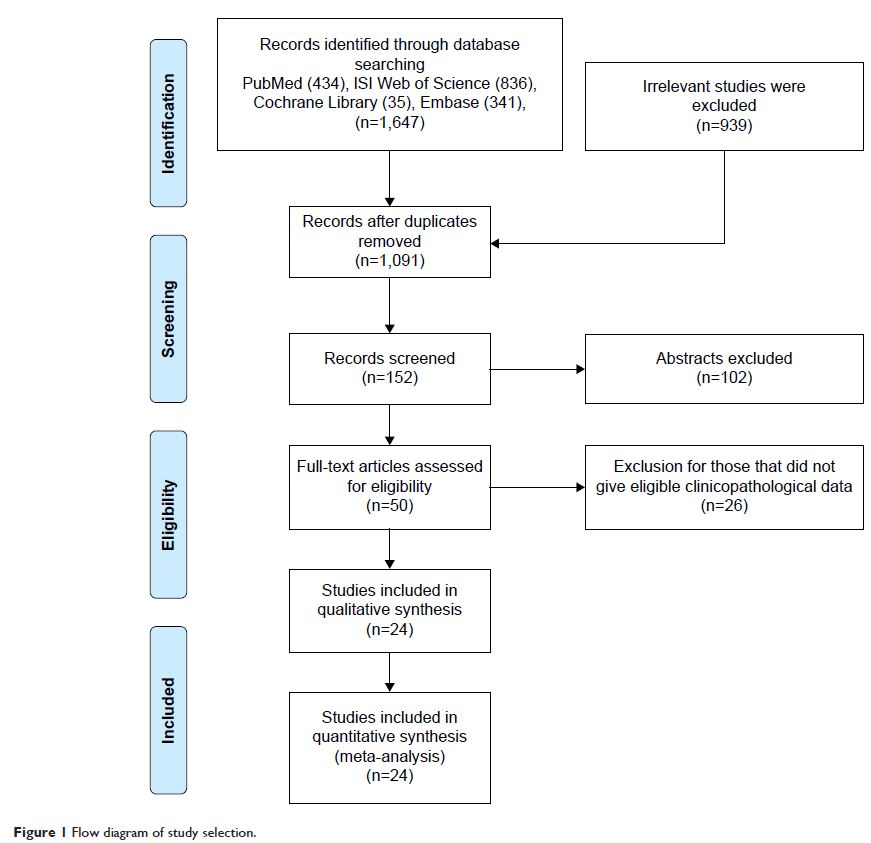
Materials and methods: A literature search was performed in PubMed,
Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Embase databases. Data on the
relationship between expression of HSPs and survival outcomes were extracted.
Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CI were calculated.
Results: The expression of HSPs was not associated with the
overall survival (OS) of GIC patients; however, it was significantly associated
with worse OS for gastric cancer (GC) and colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
Conclusion: Current evidence suggests that a high level of
HSPs may not be a potential marker to predict the survival rate for every type
of GICs. However, the expression of HSPs may predict a poor prognosis for GC
and CRC patients.
Keywords: heat shock
protein, gastrointestinal cancer, prognosis, meta-analysis