111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在白蛋白和氧化石墨烯双载体上开发生物相容性和 VEGF 靶向紫杉醇纳米药物,用于体外和体内光热触发药物递送
Authors Deng W, Qiu J, Wang S, Yuan Z, Jia Y, Tan H, Lu J, Zheng R
Received 6 September 2017
Accepted for publication 24 October 2017
Published 17 January 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 439—453
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S150977
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
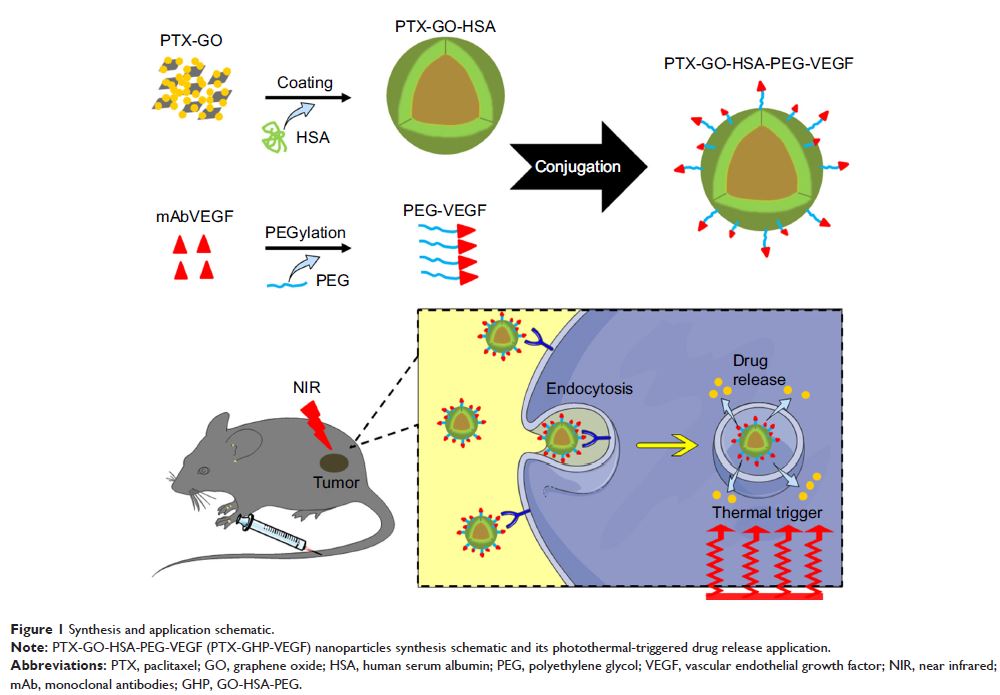
Abstract: In this study, we performed the characterization and synthesis of
biocompatible and targeted albumin and graphene oxide (GO) dual-carrier
paclitaxel (PTX) nanoparticles for photothermal-triggered tumor therapy. PTX
absorbed on GO nanosheets as cores were coated with human serum albumin (HSA),
following surface conjugation with monoclonal antibodies (mAb) against vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF; denoted as mAbVEGF) via polyethylene glycol
linker to form targeted nanoparticles (PTX-GHP-VEGF). The spherical
nanoparticles were 191±5 nm in size with good stability and biocompatibility.
GO functioned as the first carrier and a near infrared absorber that can
generate photothermal effects under 5-minute 808-nm laser irradiation to thermal
trigger the release of PTX from the second carrier HSA nanoparticles. The
mechanism of thermal-triggered drug release was also investigated
preliminarily, in which the heat generated by GO induced swelling of
PTX-GHP-VEGF nanoparticles which released the drugs. In vitro studies found
that PTX-GHP-VEGF can efficiently target human SW-13 adrenocortical carcinoma
cells as evaluated by confocal fluorescence microscopy as well as transmission
electron microscopy, and showed an obvious thermal-triggered antitumor effect,
mediated by apoptosis. Moreover, PTX-GHP-VEGF combined with near infrared
irradiation showed specific tumor suppression effects with high survival rate
after 100 days of treatment. PTX-GHP-VEGF also demonstrated high biosafety with
no adverse effects on normal tissues and organs. These results highlight the
remarkable potential of PTX-GHP-VEGF in photothermal controllable tumor
treatment.
Keywords: paclitaxel,
graphene oxide, human serum albumin, tumor targeting, photothermal-triggered
tumor therapy