111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

生物可诱导纳米胶囊用于叶酸辅助的靶向用药及有效的肿瘤特异性化疗
Authors Yi Q, Ma J, Kang K, Gu Z
Received 18 August 2017
Accepted for publication 7 December 2017
Published 31 January 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 653—667
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S149458
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Eytan Klausner
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
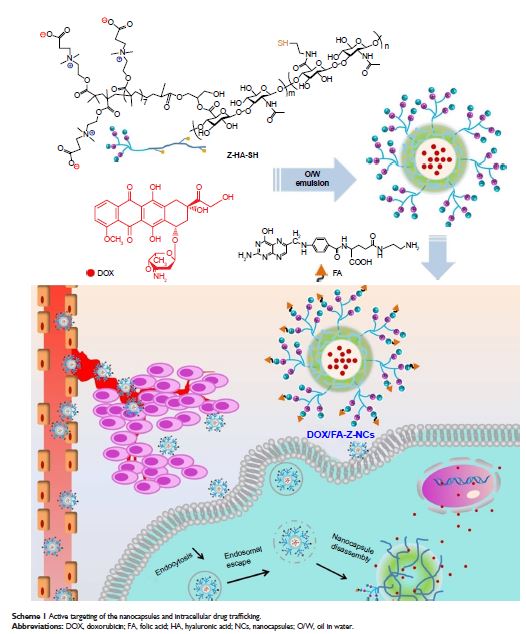
Introduction: Increasing demands in precise
control over delivery and functionalization of therapeutic agents for tumor-specific
chemotherapy have led to a rapid development in nanocarriers. Herein, we report
a nanocapsule (NC) system for tumor-oriented drug delivery and effective tumor
therapy.
Materials and methods: Functionalized hyaluronan is utilized to build up the
NC shells, in which bioreduction cleavable sites, targeting ligand folic acid
(FA), and zwitterionic tentacles are integrated.
Results: The hollow NCs obtained (~50 nm in diameter) showed
well-defined spherical shell structures with a shell thickness of ~8 nm. These
specially designed NCs (doxorubicin [DOX]/FA-Z-NCs) with high drug
encapsulation content exhibited good biocompatibility in vitro and fast
intracellular drug release behavior mediated by intracellular glutathione.
Conclusion: Cellular uptake tests demonstrated rapid uptake of
these functionalized NCs and effective escape from endosomes. Antitumor
efficacy of the DOX/FA-Z-NCs was confirmed by the significant tumor growth
inhibition effect as well as greatly reduced side effects, in contrast with
those of the free drug DOX hydrochloride.
Keywords: drug delivery,
active targeting, zwitterionic poly(carboxybetaine methacrylate), doxorubicin