111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-1180-5p 通过靶向 p73 调节维尔姆斯肿瘤的细胞凋亡
Authors Jiang X, Li H
Received 9 August 2017
Accepted for publication 19 October 2017
Published 16 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 823—831
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S148684
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Introduction: Wilms’ tumor (WT), the
most common childhood tumor, occurs in sporadic or familial forms. Recent
findings reported that abnormal expression in microRNA (miRNA) suggests an
important role of miRNAs during WT progress. MiRNAs are endogenous short-chain
noncoding RNAs, which have been reported as key biomarkers for detecting tumor
onset and progression. However, the functional role of miR-1180 in WT has
remained unknown.
Materials and methods: MTT and clonogenic survival assays were used to
detect WT cell proliferation. Flow cytometry Annexin V-FITC was used to measure
apoptosis. In addition, proteins expressions in the cells were determined by
Western blotting.
Results: In the present study, we demonstrated that
miR-1180 is upregulated in WT when compared with adjacent tissues by
quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. In addition, the
inhibition of miR-1180 induced apoptosis in SK-NEP-1 cell line in vitro.
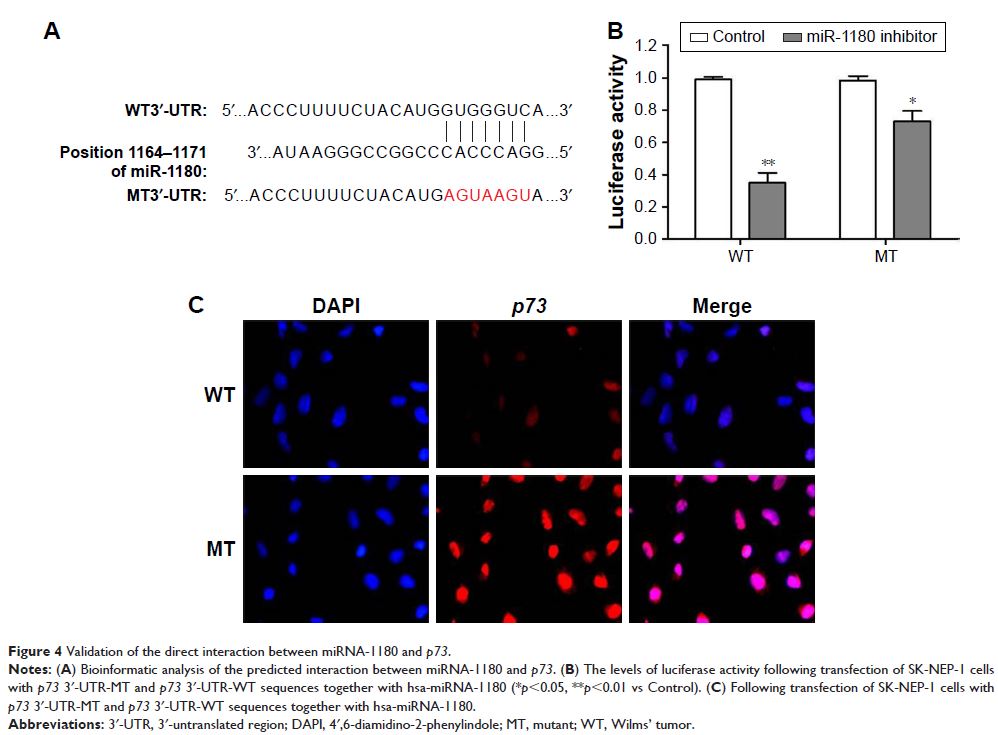
Moreover, luciferase reporter assay showed that p73 protein was the target of
miR-1180, which was confirmed by the results of Western blotting. Finally, in
vivo data indicated that the tumor growth in mice was significantly inhibited
by miR-1180 inhibitor.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that miR-1180 might serve as a
therapeutic target for future WT therapy.
Keywords: miR-1180-5p,
childhood tumor, apoptosis, p73 , cell
signaling, microRNA