111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

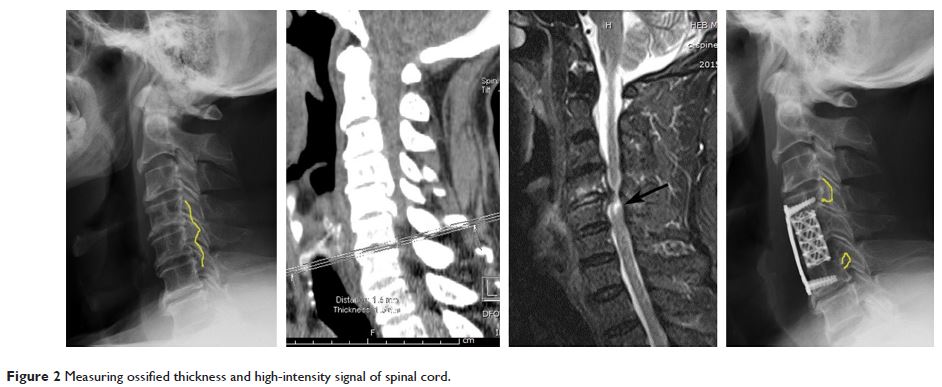
前纵韧带骨化症患者前路手术后预后不良的潜在危险因素
Authors Li SQ, Zhang P, Gao XD, Miao DC, Gao YL, Shen Y
Received 23 September 2017
Accepted for publication 15 January 2018
Published 20 February 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 341—347
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S152416
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: Our
purpose here was to identify risk factors of poor outcome after anterior
operation in patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal
ligament (OPLL).
Methods: This study retrospectively reviewed 98 patients who underwent anterior
surgery for improving neurological symptoms. The Japanese Orthopedic
Association (JOA) recovery rate <50% was defined as poor surgical outcome.
We investigated the relationship between various predictors and outcome by
logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic curves. To
explore the cause of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage, we used the
Mann–Whitney U -test, χ 2 test, or independent t -test.
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age (odds
ratio [OR] =1.1, 95% confidence interval [CI] =1.03–1.18, P =0.005), occupying ratio of
OPLL (OR =1.08, 95% CI =1.03–1.12, P =0.001), and
residual ratio of OPLL (OR =1.07, 95% CI =1.02–1.13, P =0.008) were independently
associated with poor outcome. The cutoffs of the above risk factors were set at
63.5 years, 39.65%, and 25.165%, respectively. Predictors for CSF leakage were
occupying ratio of OPLL, the K-line, and shape of the ossified lesion (P <0.001, P =0.019, and P =0.003).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that advanced age, high occupying ratio of
OPLL, and high residual ratio of OPLL were risk factors for postoperative poor
outcome in patients with OPLL. In addition, the high occupying ratio of OPLL,
the K-line (-), and hill-shape ossification were potential causes of CSF
leakage.
Keywords: cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament,
cerebrospinal leakage, occupying ratio, residual ratio, K-line