111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:一种新的利用结冷胶的布林佐胺眼部递送:体外和体内评估
Authors Sun J, Zhou Z
Received 6 October 2017
Accepted for publication 30 November 2017
Published 23 February 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 383—389
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S153405
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Junhua Mai
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: The aim of the study
was to develop a sustained ocular delivery of brinzolamide (BLZ) based on
gellan gum.
Methods: The formulations were characterized for clarity,
gelling capacity, rheological studies, pH, drug content, and in vitro
drug-release behavior. In vivo rabbit eye irritation test was conducted to
evaluate irritation of the BLZ gel drug-delivery system. The prepared BLZ
formulations were then investigated in vivo and compared with commercially
available BLZ eyedrops with regard to pharmacodynamics.
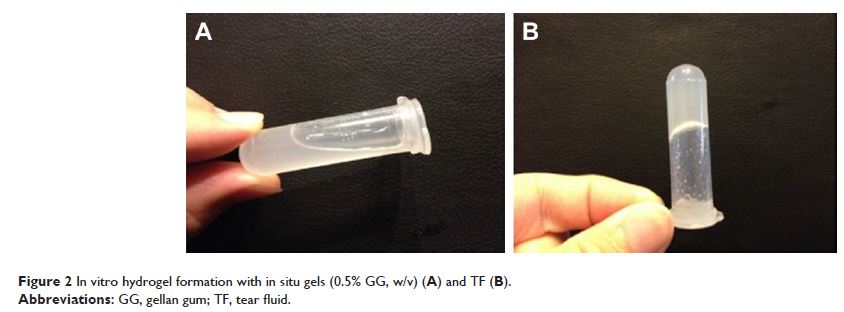
Results: The results showed that the optimum
concentration of gellan gum was 0.25% w/v; the prepared liquid was converted
into a flowing gel after the addition of simulated tear fluid. In vitro release
profiles showed that the release of BLZ from the in situ gel exhibited
sustained characteristics. Draize test results showed that BLZ in situ gels did
not stimulate signs of eye tissue activity and were less irritating than BLZ
solutions and commercial Azopt.
Conclusion: The results of pharmacodynamics implied that the
novel preparation of BLZ in situ gel effectively prolonged the intraocular
pressure-lowering effect after administration.
Keywords: in situ gel,
ion sensitive, glaucoma, ocular drug delivery, sustained release