108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丙型肝炎病毒核通过调控 TGFBRAP1 和 HOTTIP 的表达影响与致癌进展有关的 miR122 和 miR204 表达
Authors Wang X, Peng J, Wang J, Li M, Wu D, Wu S, Liao J, Dou J
Received 16 August 2017
Accepted for publication 27 December 2017
Published 2 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1173—1182
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149254
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Despite the breadth of understanding the noncoding RNAs’ function in
molecular biology, their functional roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is
poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the effect of hepatitis C
virus (HCV) core upon the expression of noncoding RNAs.
Methods: The lncRNAs, mRNAs, and circRNAs were employed for identification
of HCV core protein gene expression in human Huh7 hepatoma (Huh7) cell line. In
data analysis, we applied a threshold that eliminated all genes that were not
increased or decreased by at least a 2-fold change in a comparison between
transfected and control cells. Hierarchical Clustering and the Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genome pathway analyses were performed to show the
distinguishable lncRNA, mRNAs, and circRNAs expression pattern among samples.
Results: The array data showed that 4,851 lncRNAs, 4,785 mRNAs, and 823 circRNAs
were 2-fold up-regulated but 3,569 lncRNAs, 3,192 mRNAs, and 419 circRNAs were
2-fold down-regulated in Huh 7-core cells. The genes in the enriched set were
associated with macromolecule and nucleic acid metabolic processes, DNA damage
response and regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel. We identified 10
genes from the selected 14 genes that were higher or lower expression in
Huh7-core cells than that of Huh7-vector cells by quantitative real-time
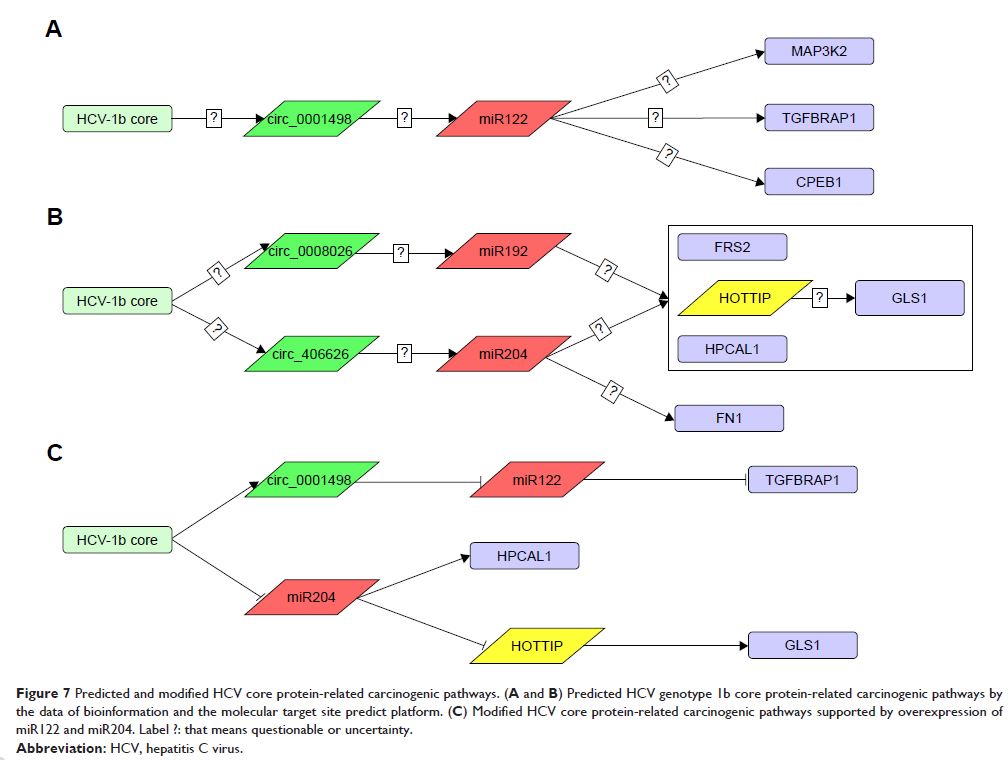
polymerase chain reaction. Interestingly, overexpression of miR122 and miR204
partly abrogated the expression of TGFBRAP1 and HOTTIP, and increased the
HPCAL1 expression in the predicted carcinogenic pathways.
Conclusion: Our data suggests that the pathways of miR204-HPCAL1-lncRNAHOTTIP and
miR122-TGFBRAP1 were likely involved in the carcinogenic progress due to the
presence of HCV core, and that overexpression of miR122 and miR204 might
inhibit the HCC progress by down-regulation of TGFBRAP1 and HOTTIP expression.
Keywords: hepatitis C virus, Core, lncRNA microarray, gene expression,
hepatocellular carcinoma, miR122, HOTTIP