111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一个横断面研究:血清 CCL3/MIP-1α 水平可以反映汉族人腰椎间盘退变
Authors Zhang YL, Li B, Zhou ZH
Received 22 September 2017
Accepted for publication 13 January 2018
Published 5 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 497—503
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S152349
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Minal Joshi
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Background: The
macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), also named chemokine cytokine
ligand 3 (CCL3), has been detected in nucleus pulposus and increased following
cytokine stimulation.
Objective: The current study was performed to explore the relationship between
serum CCL3/MIP-1α levels with lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration (IDD).
Patients and
methods: A total of 132 disk degeneration
patients confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging and 126 healthy controls were
enrolled in the current study. Radiological evaluation of the IDD was conducted
using a 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging scanner for entire lumbar vertebra
region. Degeneration of intervertebral disk was assessed by Schneiderman
criteria. Serum CCL3/MIP-1α levels were investigated using a sandwich
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The Visual Analog Scale scores and Oswestry
Disability Index index were recorded for clinical severity.
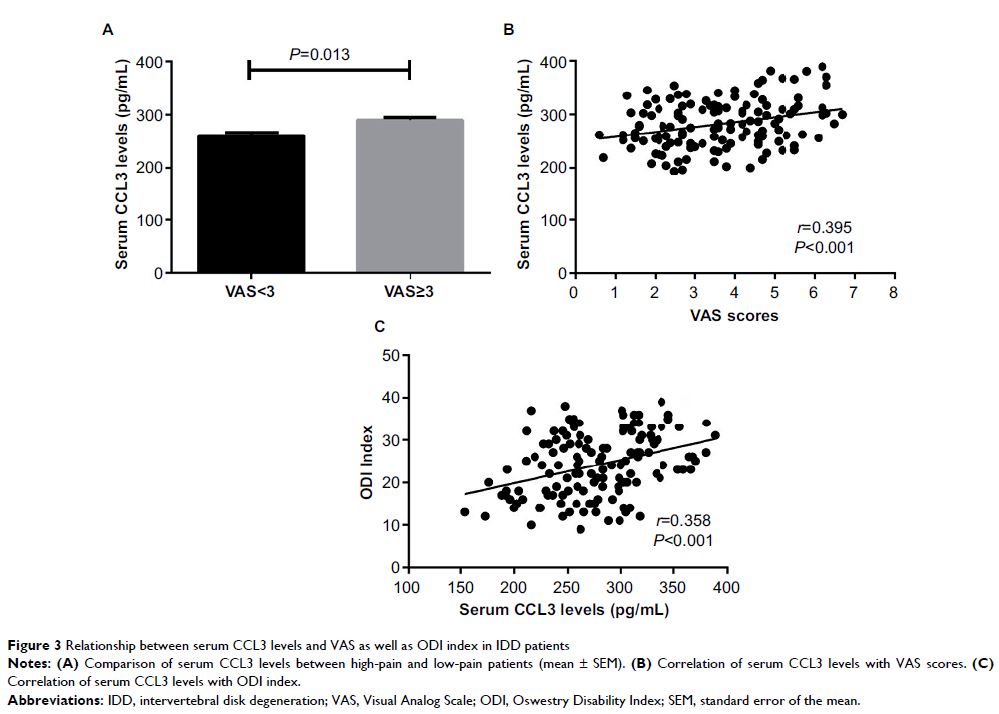
Results: Elevated concentrations of CCL3 in serum were found in IDD patients
compared with asymptomatic volunteers. The case group included 49 IDD patients
with grade 1, 42 with grade 2, and 41 with grade 3. Grade 3 and 2 had
significantly higher CCL3 concentrations in serum compared with those with
grade 1. The serum CCL3 levels were positively related to the degree of disk
degeneration. In addition, the serum CCL3 levels also demonstrated a
significant correlation with the clinical severity determined by Visual Analog
Scale scores and Oswestry Disability Index index.
Conclusion: Serum CCL3 may serve as a biomarker of IDD.
Keywords: chemokine cytokine ligand 3, intervertebral disk degeneration,
cross-sectional study