111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

HSP27 在肝细胞癌中的临床病理及预后价值:一项系统综述和荟萃分析
Authors Liang CJ, Xu YC, Ge H, Li GM, Wu JX
Received 16 October 2017
Accepted for publication 26 January 2018
Published 7 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1293—1303
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154227
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Manfred Beleut
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Background: In the recent past, there is increasing evidence demonstrating that
HSP27 plays a key role in tumor progression. However, the relationship between
HSP27 expression and the clinicopathological features of hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC), as well as its prognostic value in HCC patients remain
controversial. Accordingly, we conducted a meta-analysis to assess the
correlation between HSP27 expression and HCC, and determine the prognostic
value of HSP27 in HCC.
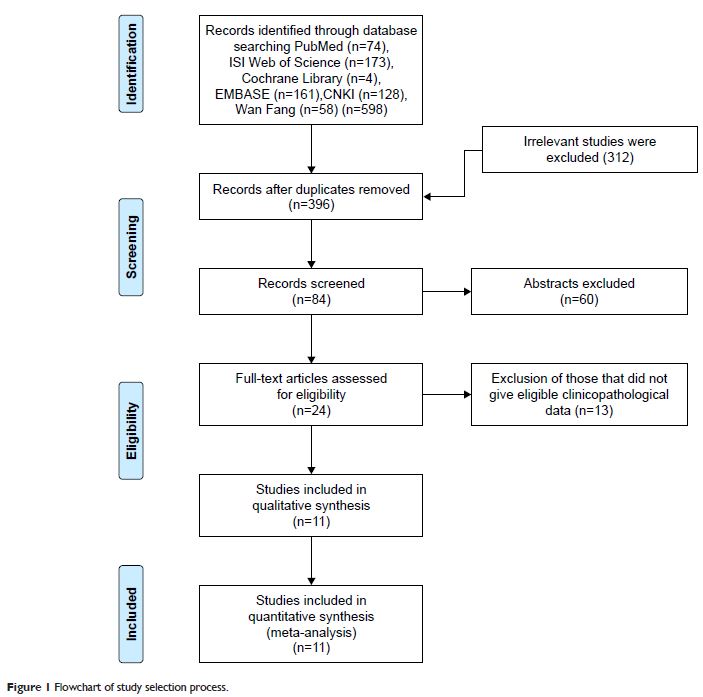
Methods: The data included clinicopathological features and survival information
extracted from the published literature in the databases PubMed, EMBASE,
Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, and Wan Fang. The pooled odds ratios
and hazard ratios with 95% CIs were calculated using Forest plot analysis.
Results: The meta-analysis results indicated that the positive HSP27 expression
was significantly correlated with HCC incidence, tumor differentiation, and
α-fetoprotein level in patients with HCC. However, the expression of HSP27 was
not associated with metastasis, hepatitis B virus surface antigen, gender,
tumor size, TNM stage, and vascular invasion. Additionally, HSP27 expression
indicated a poor overall survival rate, but it was not related to disease-free
survival rate.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis revealed that HSP27 may play a key role in the
development of HCC and could be a reliable biomarker for the prognosis of
patients with HCC. However, additional high-quality research is needed to
support the results.
Keywords: HCC, heat shock protein 27, meta-analysis