108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于靶向递送 pH 敏感性甲氨蝶呤前体药物的姜黄素纳米颗粒旨在进行双药物高效递送,是组合性癌症疗法的一部分
Authors Xie JJ, Fan ZX, Li Y, Zhang YY, Yu F, Su GH, Xie LY, Hou ZQ
Received 22 September 2017
Accepted for publication 11 January 2018
Published 9 March 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1381—1398
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S152312
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
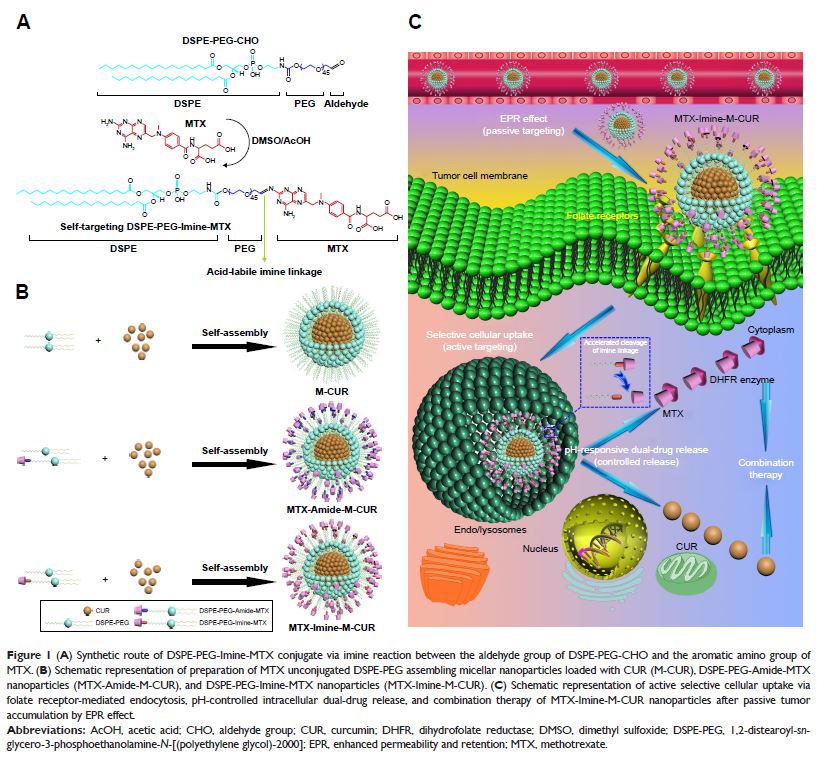
Aim: We designed acid-labile methotrexate (MTX) targeting prodrug
self-assembling nanoparticles loaded with curcumin (CUR) drug for simultaneous
delivery of multi-chemotherapeutic drugs and combination cancer therapy.
Methods: A dual-acting MTX, acting as both an anticancer drug and as a
tumor-targeting ligand, was coupled to
1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[aldehyde(polyethylene
glycol)-2000] via Schiff’s base reaction. The synthesized prodrug conjugate
(DSPE-PEG-Imine-MTX) could be self-assembled into micellar nanoparticles
(MTX-Imine-M) in aqueous solution, which encapsulated CUR into their core by
hydrophobic interactions (MTX-Imine-M-CUR).
Results: The prepared MTX-Imine-M-CUR nanoparticles were composed of an inner
hydrophobic DSPE/CUR core and an outside hydrophilic bishydroxyl poly (ethyleneglycol)
(PEG) shell with a self-targeting MTX prodrug corona. The imine linker between
1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[aldehyde(polyethyleneglycol)-2000]
and MTX, as a dynamic covalent bond, was strong enough to remain intact in physiological
pH, even though it is rapidly cleaved in acidic pH. The MTX-Imine-M-CUR could
codeliver MTX and CUR selectively and efficiently into the cancer cells via
folate receptor-mediated endocytosis followed by the rapid intracellular
release of CUR and the active form of MTX via the acidity of
endosomes/lysosomes. Moreover, the MTX-Imine-M-CUR resulted in significantly
higher in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity than pH-insensitive
DSPE-PEGAmide-MTX assembling nanoparticles loaded with CUR (MTX-Amide-M-CUR),
MTX unconjugated DSPE-PEG assembling micellar nanoparticles loaded with CUR
(M-CUR), combination of both free drugs, and individual free drugs.
Conclusion: The smart system provided a simple, yet feasible, drug delivery
strategy for targeted combination chemotherapy.
Keywords: pH-sensitive prodrug, self-assembly, targeting, combination
therapy, nanoparticles