111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
L61H46 通过抑制 STAT3 途径展现了对人胰腺癌的有效功效
Authors Bai E, Yang L, Xiang Y, Hu W, Li C, Lin J, Dai X, Liang G, Jin R, Zhao C
Received 6 December 2017
Accepted for publication 25 January 2018
Published 23 March 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 565—581
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S159090
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
Background: Pancreatic
cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. The poor
prognosis of this disease highlights the urgent need to develop more effective
therapies. Activation of the STAT3 represents a potential drug target for
pancreatic cancer therapy. Currently, clinically available small-molecule
inhibitors targeting STAT3 are lacking.
Methods: Through bioassay screening and molecular docking, we identified a small molecule L61H46 that can potently target constitutive STAT3 signaling and kill human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
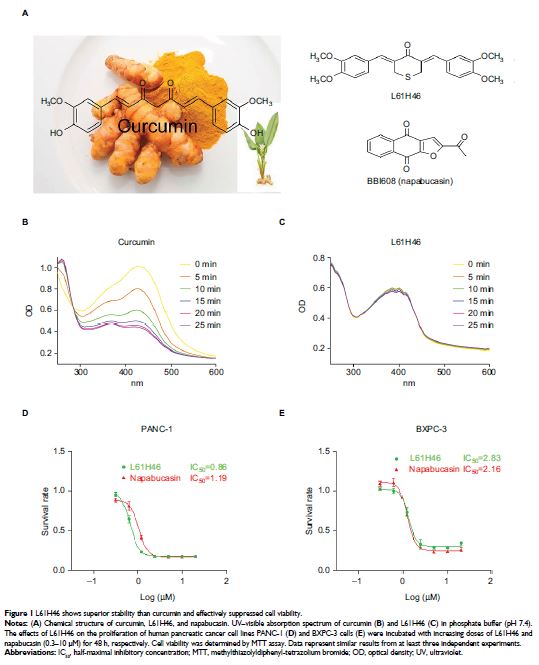
Results: L61H46 effectively reduced colony formation and the viability of pancreatic cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values in the range between 0.86 and 2.83 µM. L61H46 significantly inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation (Tyr705) and the subsequent nucleus translocation but did not downregulate STAT1 phosphorylation. Moreover, L61H46 demonstrated a potent activity in suppressing pancreatic tumor growth in BXPC-3 xenograft model in vivo. Furthermore, L61H46 showed no signs of adverse effects on liver, heart, and kidney cells in vivo.
Conclusion: Collectively, our results suggest that L61H46 could be further optimized into a highly potent STAT3 inhibitor for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: L61H46, STAT3, cancer therapy, interleukin-6, pancreatic cancer
Methods: Through bioassay screening and molecular docking, we identified a small molecule L61H46 that can potently target constitutive STAT3 signaling and kill human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
Results: L61H46 effectively reduced colony formation and the viability of pancreatic cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values in the range between 0.86 and 2.83 µM. L61H46 significantly inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation (Tyr705) and the subsequent nucleus translocation but did not downregulate STAT1 phosphorylation. Moreover, L61H46 demonstrated a potent activity in suppressing pancreatic tumor growth in BXPC-3 xenograft model in vivo. Furthermore, L61H46 showed no signs of adverse effects on liver, heart, and kidney cells in vivo.
Conclusion: Collectively, our results suggest that L61H46 could be further optimized into a highly potent STAT3 inhibitor for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: L61H46, STAT3, cancer therapy, interleukin-6, pancreatic cancer