108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

经冰片修饰的化学固体脂质纳米粒子可增强血脑屏障的通透性和脑靶向功能
Authors Song H, Wei M, Zhang N, Li H, Tan XC, Zhang YJ, Zheng WS
Received 1 January 2018
Accepted for publication 17 February 2018
Published 28 March 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1869—1879
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S161237
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: The
incidence of central nervous system disease has increased in recent years.
However, the transportation of drug is restricted by the blood–brain barrier,
contributing to the poor therapeutic effect in the brain. Therefore, the
development of a new brain-targeting drug delivery system has become the
hotspot of pharmacy.
Materials and
methods: Borneol, a simple bicyclic
monoterpene extracted from Dryobalanops aromatica ,
can direct drugs to the upper body parts according to the theory of traditional
Chinese medicine. Dioleoyl phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) was chemically modified
by borneol as one of the lipid materials of solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) in
the present study.
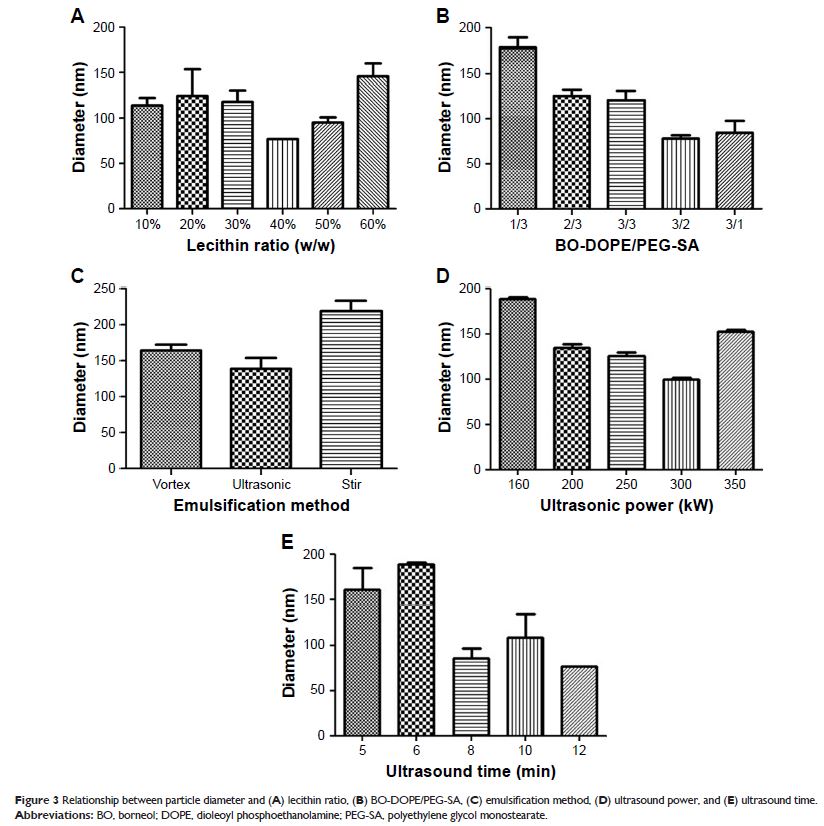
Results: The borneol-modified chemically solid lipid nanoparticle
(BO-SLN/CM), borneol-modified physically solid lipid nanoparticle (BO-SLN/PM),
and SLN have similar diameter (of about 87 nm) and morphological
characteristics. However, BO-SLN/CM has a lower cytotoxicity, higher cell
uptake, and better blood–brain barrier permeability compared with BO-SLN/PM and
SLN. BO-SLN/CM has a remarkable targeting function to the brain, while
BO-SLN/PM and SLNs are concentrated at the lung.
Conclusion: The present study provides an excellent drug delivery carrier,
BO-SLN/CM, having the application potential of targeting to the brain and
permeating to the blood–brain barrier.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier, solid lipid nanoparticle, phospholipid
modification, BBB model in vitro, body distribution