108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过摩擦搅拌加工制备的新型 Ti-6V-4V/锌表面纳米复合材料的微结构及机械和生物特性
Authors Zhu C, Lv Y, Qian C, Ding Z, Jiao T, Gu X, Lu E, Wang L, Zhang F
Received 17 October 2017
Accepted for publication 15 January 2018
Published 28 March 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1881—1898
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S154260
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Bhavesh Kevadiya
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: The interaction between the material and the organism affects the
survival rate of the orthopedic or dental implant in vivo. Friction stir
processing (FSP) is considered a new solid-state processing technology for
surface modification.
Purpose: This study aims to strengthen the surface mechanical properties
and promote the osteogenic capacity of the biomaterial by constructing a
Ti-6Al-4V (TC4)/zinc (Zn) surface nanocomposites through FSP.
Methods: FSP was used to modify the surface of TC4. The microstructures and
mechanical properties were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy,
transmission electron microscopy, nanoindentation and Vickers hardness. The
biological properties of the modified surface were evaluated by the in vitro
and in vivo study.
Results: The results showed that nanocrystalline and numerous β regions, grain
boundary a phase, coarser acicular α phase and finer acicular martensite α'
appeared because of the severe plastic deformation caused by FSP, resulting in
a decreased elastic modulus and an increased surface hardness. With the
addition of Zn particles and the enhancement of hydrophilicity, the
biocompatibility was greatly improved in terms of cell adhesion and
proliferation. The in vitro osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow
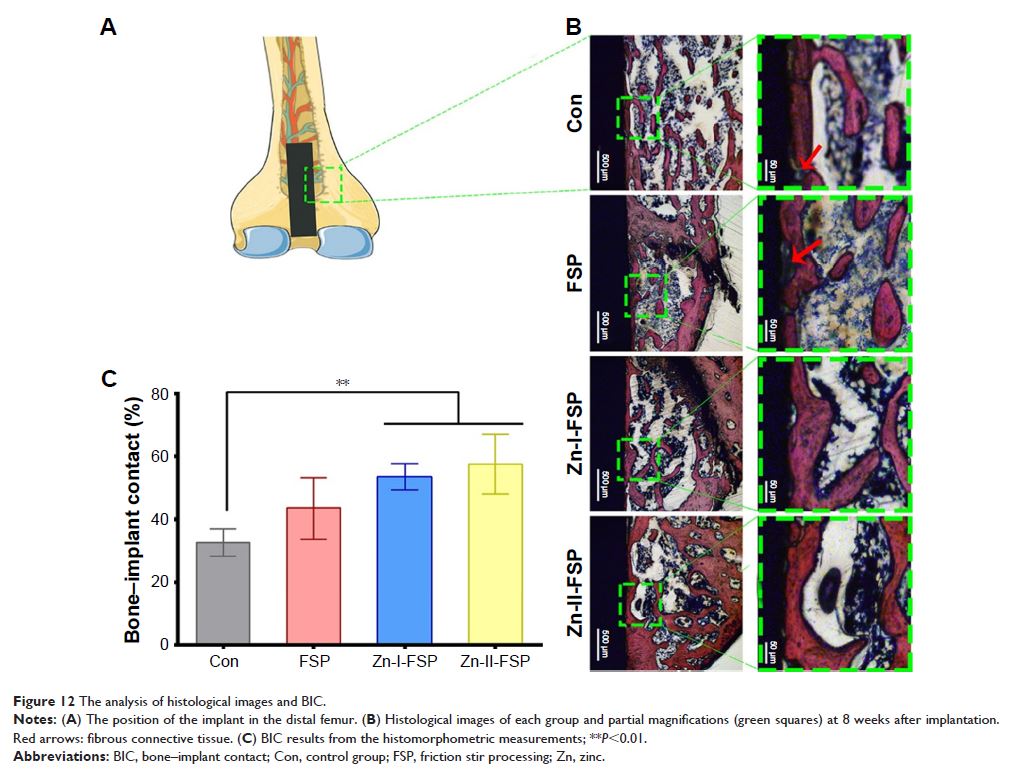
stromal cells and rapid in vivo osseointegration were enhanced on the novel
TC4/Zn metal matrix nanocomposite surface.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that this novel TC4/Zn surface nanocomposite
achieved by FSP has significantly improved mechanical properties and
biocompatibility, in addition to promoting osseointegration and thus has
potential for dental and orthopedic applications.
Keywords: nanocomposite, friction stir processing, nanocrystalline/ultrafine
grained, bone marrow stromal cells, cell proliferation, osteogenic
differentiation