108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Ki-67 增殖标志物的表达与转化生长因子 B1 有关,可以预测肝病毒相关肝细胞癌患者的预后
Authors Yang C, Su H, Liao X, Han C, Yu T, Zhu G, Wang X, Winkler CA, O'Brien SJ, Peng T
Received 15 January 2018
Accepted for publication 9 February 2018
Published 10 April 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 679—696
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S162595
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
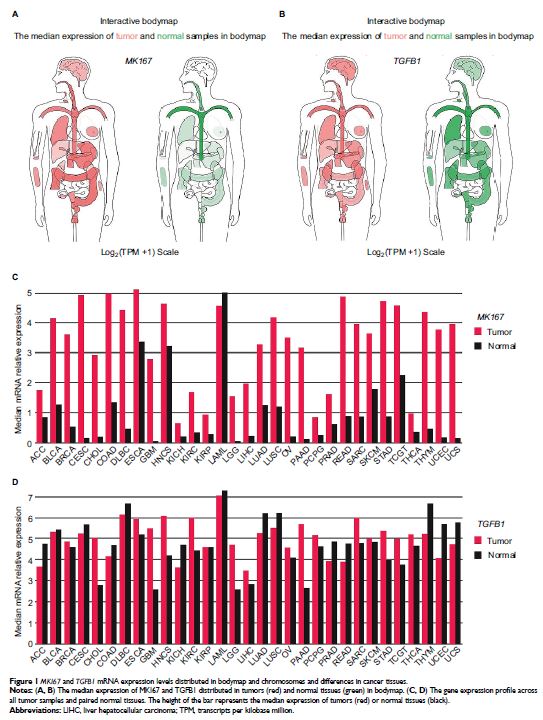
Abstract: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most frequent malignancy of the
liver. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB1 ) and marker
of proliferation Ki-67 (MKI67 ) regulate
cell proliferation, differentiation, and growth. The association between MKI67
and TGFB1 expression and its clinical implications in HCC remain unknown.
Methods: Public databases were used to analyze TGFB1 and MKI67 expression
in different pathologic grades/stages and tissue types of HCC. The association
between MKI67 and TGFB1 expression was explored using pathway analysis and in a
HepG2 cell line treated with TGFB1. Survival analysis was performed to evaluate
the prognostic value of TGFB1 and MKI67 expression in patients with hepatitis B
virus (HBV)-related HCC.
Results: We identified that MKI67 expression was upregulated in liver
cancer tissues. MKI67 and TGFB1 expression levels were different in various
stages and tissue types of liver cancer. Furthermore, MKI67 expression was associated
with TGFB1 expression in liver cancer tissues and HepG2 cells. Patients with
HBV-related HCC and a higher level of MKI67 expression had a worse prognosis.
Moreover, a nomogram was conducted to predict the clinical outcomes of patients
with HBV-related HCC.
Conclusion: MKI67 expression level was associated with TGFB1 expression in liver
cancer tissues and a HepG2 cell line. MKI67 expression level can predict the
clinical outcomes of patients with HBV-related HCC.
Keywords: MKI67, TGFB1, HBV-related HCC, nomogram