108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 M2 型丙酮酸激酶的微小类泛素化修饰可在 A549 人肺癌细胞中促进有氧糖酵解和细胞增殖
Authors An S, Huang L, Miao P, Shi L, Shen M, Zhao X, Liu J, Huang G
Received 13 November 2017
Accepted for publication 18 January 2018
Published 13 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2097—2109
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156918
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Objective: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide.
Aerobic glycolysis is considered the seventh hallmark of cancer. The M2 isoform
of pyruvate kinase (PKM2) is an important rate-limiting enzyme in glycolytic
pathway, and is strongly expressed in several types of cancer. Thus,
understanding the underlying mechanisms of regulation of PKM2 is of great value
for targeted therapy for lung cancer.
Patients and
methods: Seventy-three lung adenocarcinoma
patients were analyzed in our study. The expression levels of PKM2 were
analyzed by immunohistochemistry on tissues. The effect of small ubiquitin-like
modifier 1 (SUMO1) on PKM2 expression was investigated using Western blot assay
and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. PKM2 SUMO1 modification was
determined by in vitro and in vivo SUMOylation assays. 18F-deoxyglucose uptake and lactate production measurements were conducted
to research the levels of glycolysis. The level of oxidative phosphorylation in
cells was determined by cellular oxygen consumption rate measurements. Cell
proliferation assays were carried out to confirm the growth ability of tumor
cells.
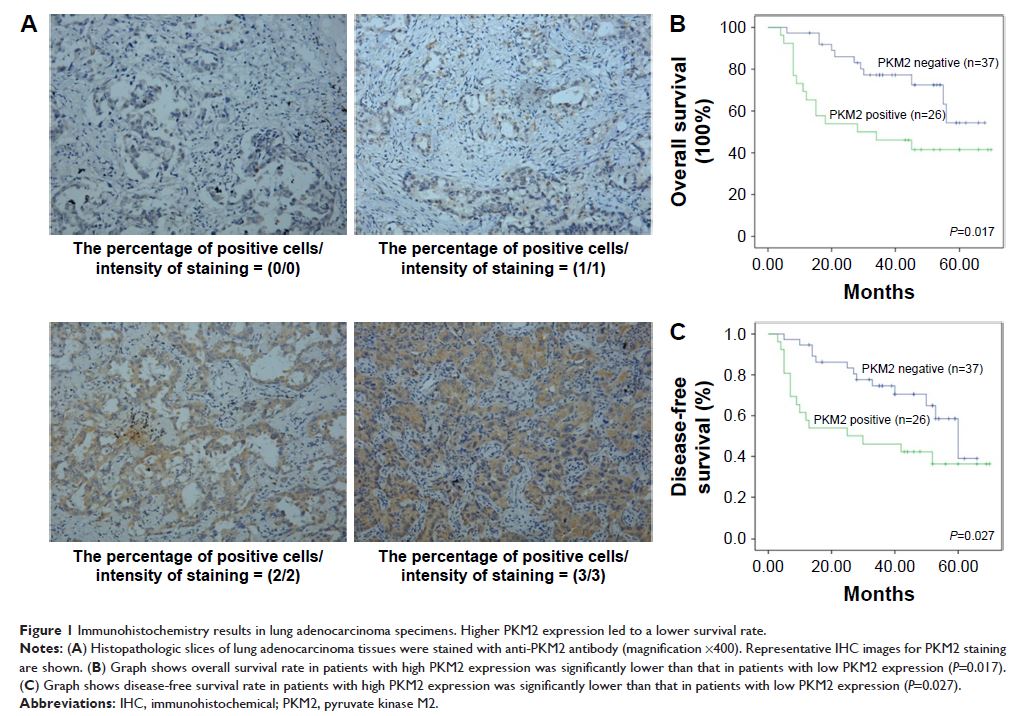
Results: PKM2 was overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma patients based on
immunohistochemical staining. Patients with high PKM2 expression had reduced
overall survival rate (P =0.017) and
disease-free survival rate (P =0.027) compared
with those with low PKM2 expression. SUMO1 promoted PKM2-dependent glycolysis.
Western blotting analysis showed that SUMO1 knockdown in A549 cells led to a
significant decrease in PKM2 protein expression. PKM2 could be covalently
modified by SUMO1 at K336 (Lys336) site. SUMO1 modification of PKM2 at Lys-336
site increased glycolysis and promoted its cofactor functions. Moreover, PKM2
SUMO1 modification promoted the proliferation of A549 cells in vitro.
Conclusion: This information is important in elucidating a new mechanism of
regulation of PKM2, and suggested that SUMO1 modification of PKM2 could be a
potential therapeutic target in lung cancer.
Keywords: Pyruvate Kinase M2, SUMO1 modification, glycolysis, cell proliferation,
cancer