108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氯胺酮通过 Nrf2 途径改善了创伤性脑损伤实验中的氧化应激诱导的细胞凋亡
Authors Liang J, Wu S, Xie W, He H
Received 16 December 2017
Accepted for publication 19 February 2018
Published 16 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 845—853
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S160046
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: Ketamine
can act as a multifunctional neuroprotective agent by inhibiting oxidative
stress, cellular dysfunction, and apoptosis. Although it has been proven to be
effective in various neurologic disorders, the mechanism of the treatment of
traumatic brain injury (TBI) is not fully understood. The aim of this study was
to investigate the neuroprotective function of ketamine in models of TBI and
the potential role of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway
in this putative protective effect.
Materials and
methods: Wild-type male mice were
randomly assigned to five groups: Sham group, Sham + ketamine group, TBI group,
TBI + vehicle group, and TBI + ketamine group. Marmarou’s weight drop model in
mice was used to induce TBI, after which either ketamine or vehicle was
administered via intraperitoneal injection. After 24 h, the brain samples
were collected for analysis.
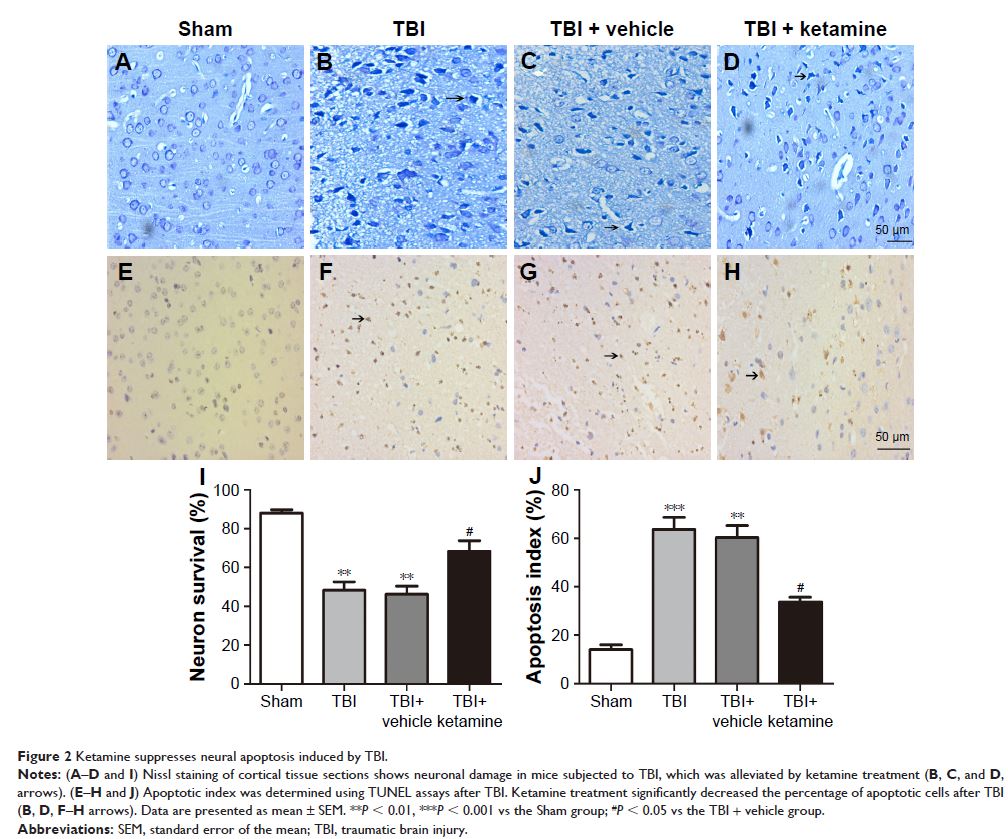
Results: Ketamine significantly ameliorated secondary brain injury induced
by TBI, including neurological deficits, brain water content, and neuronal
apoptosis. In addition, the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione
peroxidase (GPx), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were restored by the ketamine
treatment. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry showed that ketamine
significantly increased the level of Nrf2. Furthermore, administration of
ketamine also induced the expression of Nrf2 pathway-related downstream
factors, including hemeoxygenase-1 and quinine oxidoreductase-1, at the pre-
and post-transcriptional levels.
Conclusion: Ketamine exhibits neuroprotective effects by attenuating oxidative
stress and apoptosis after TBI. Therefore, ketamine could be an effective
therapeutic agent for the treatment of TBI.
Keywords: traumatic brain injury, ketamine, oxidative stress, Nrf2,
apoptosis