108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

头孢硫脒用于血液感染儿童治疗的群体药代动力学和剂量优化
Authors Zhi LJ, Wang L, Chen XK, Zhai XY, Wen L, Dong L, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Shi ZR, Zhao W
Received 19 December 2017
Accepted for publication 7 March 2018
Published 17 April 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 855—862
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S160329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Cefathiamidine, a first-generation cephalosporin, has approval from the
China Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of infections caused by
susceptible bacteria in both adults and children. As pharmacokinetic data are
limited in the pediatric population, we aimed to evaluate the population
pharmacokinetics of cefathiamidine in children and to define the appropriate
dose in order to optimize cefathiamidine treatment.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from children treated with
cefathiamidine, and concentrations were quantified by high-performance liquid
chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Population pharmacokinetic
analysis was conducted using NONMEM software.
Results: Fifty-four children (age range: 2.0–11.8 years) were included. Sparse
pharmacokinetic samples (n=120) were available for analysis. A two-compartment
model with first-order elimination showed the best fit with the data. A
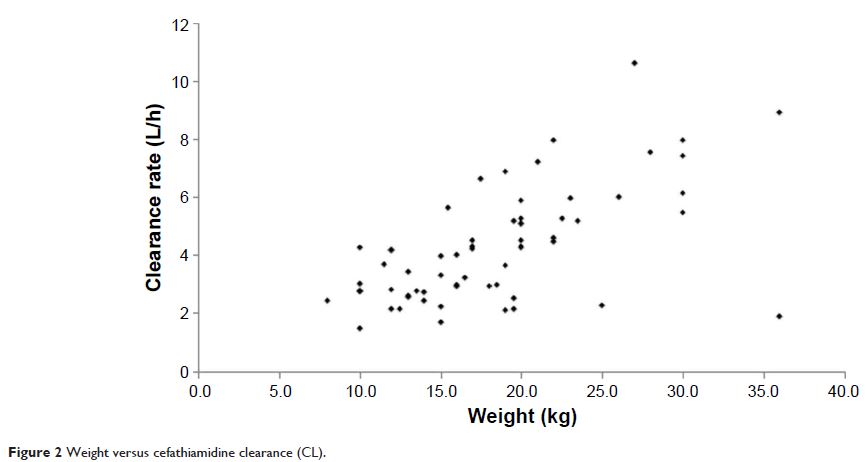
covariate analysis identified that bodyweight had a significant impact on
cefathiamidine pharmacokinetics. Monte Carlo simulation demonstrated that the
currently used dosing regimen of 100 mg/kg/day q12h was associated with a
high risk of underdosing in pediatric patients. To reach the target 70%
fT>MIC, a dose of 100 mg/kg/day cefathiamidine q6h is required for
effective treatment against Haemophilus influenzae .
Conclusion: A population pharmacokinetics model of cefathiamidine in children with
hematologic disease was established. A dosing regimen of 100 mg/kg/day
cefathiamidine q6h should be used in clinical practice against H. influenza infections.
Keywords: cefathiamidine, pharmacokinetics, dosing, children