111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于金纳米粒子的比色法检测前列腺特异性抗原
Authors Xia N, Deng D, Wang Y, Fang C, Li S
Received 13 October 2017
Accepted for publication 24 January 2018
Published 24 April 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2521—2530
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S154046
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
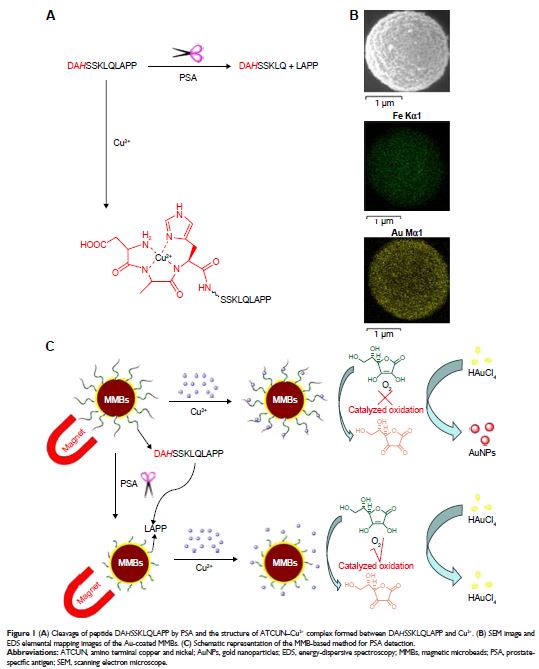
Background: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a serine protease, is a biomarker
for preoperative diagnosis and screening of prostate cancer and monitoring of
its posttreatment.
Methods: In
this work, we reported a colorimetric method for clinical detection of PSA
using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as the reporters. The method is based on
ascorbic acid (AA)-induced in situ formation of AuNPs and Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of AA. Specifically, HAuCl4 can be reduced into AuNPs by AA; Cu2+ ion can catalyze the oxidation of AA by O2 to inhibit the formation of AuNPs. In the
presence of the PSA-specific peptide (DAH SSKLQLAPP)-modified
gold-coated magnetic microbeads (MMBs; denoted as DAH SSKLQLAPP-MMBs),
complexation of Cu2+ by the MMBs through the
DAH–Cu2+ interaction depressed the catalyzed oxidation
of AA and thus allowed for the formation of red AuNPs. However, once the
peptide immobilized on the MMB surface was cleaved by PSA, the DAH SSKLQ segment would be released.
The resultant LAPP fragment remaining on the MMB surface could not sequestrate
Cu2+ to depress its catalytic activity toward AA
oxidation. Consequently, no or less AuNPs were generated.
Results: The linear range for PSA detection was found to be
0~0.8 ng/mL with a detection limit of 0.02 ng/mL. Because of the separation of
cleavage step and measurement step, the interference of matrix components in
biological samples was avoided.
Conclusion: The high extinction coefficient of AuNPs
facilitates the colorimetric analysis of PSA in serum samples. This work is
helpful for designing of other protease biosensors by matching specific peptide
substrates.
Keywords: colorimetric
assay, gold nanoparticles, prostate-specific antigen, ascorbic acid, Cu2+ ion