111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

circ_0066444 上调可促进胃癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Rong D, Dong C, Fu K, Wang H, Tang W, Cao H
Received 8 November 2017
Accepted for publication 7 February 2018
Published 11 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2753—2761
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156516
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs), which have closed-loop structure, are involved
in the pathogenesis of human diseases including various types of carcinomas.
The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between a new circular
RNA named circ_0066444 and gastric cancer (GC) carcinogenesis.
Materials and
methods: The circ_0066444 levels in 106
paired gastric carcinoma tissues and related adjacent normal tissues were
detected by real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain
reaction. The correlation between the expression of circ_0066444 and
clinicopathological features was analyzed. The impact of circ_0066444
expression on cell proliferation, invasion, as well as migration was evaluated
in vitro using knockdown expression strategies. Finally, a network of
circ_0066444-targeted miRNA interactions and their corresponding mRNAs was
constructed.
Results: circ_0066444 was found to be significantly upregulated in 106 GC
tissues as compared with paired adjacent nontumorous tissues (P =0.025), showing a high positive
correlation with lymphatic metastasis (P =0.023).
Furthermore, in vitro assays of the GC cell lines BGC-823 and AGS demonstrated
that knockdown of circ_0066444 reduced cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration significantly. Prediction and annotation revealed circ_0066444 was
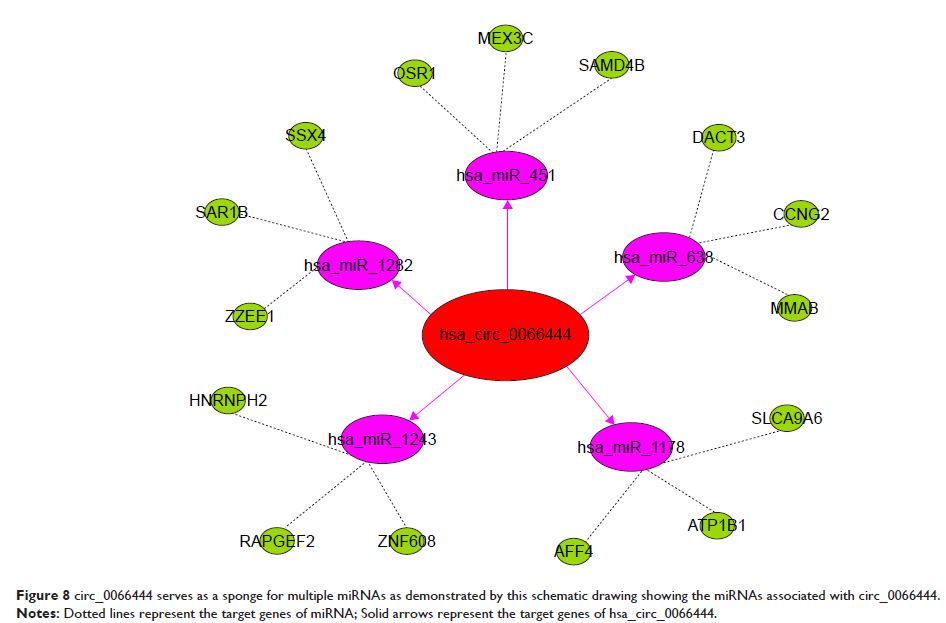
able to sponge to 5 miRNAs and 15 corresponding target mRNAs.
Conclusion: Our study indicated upregulation of circ_0066444 promotes gastric
cell proliferation, invasion, and migration ability and might serve as a novel
biomarker for GC.
Keywords: migration, invasion, proliferation, diagnoses, miRNA