111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ZNF418 过度表达可预防胃癌并提示预后良好
Authors Hui H, Hu Z, Jiang C, Wu J, Gao Y, Wang X
Received 25 December 2017
Accepted for publication 19 March 2018
Published 11 May 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2763—2770
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S160802
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: This study aimed to investigate the prognostic power of zinc-finger
protein 418 (ZNF418 ) in gastric cancer (GC) and
its potential role in GC development and progression.
Patients and
methods: A total of 10 GC patients’ individual
plasmas were collected and screened for dysregulated mRNA using human
microarray. Among these dysregulated mRNAs, ZNF418 was
found to be significantly downregulated in IIIA–IV stage GC patients compared
to IA–IIA stage GC patients. Subsequently, the ZNF418 levels
were detected by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
in both GC plasmas and tissues in a larger sample, and the association
between ZNF418 expression level and
clinicopathological features as well as overall survival (OS) of GC patients
was further analyzed. Finally, a network of ZNF418 interactions
with other molecules was predicated in STRING and GEPIA databases.
Results: Human mRNA microarray was performed to screen for abnormally expressed
mRNAs between five IIIA–IV stage GC patients’ plasma and five IA–IIA stage GC
patients’ plasma. A total of 662 mRNAs were differentially expressed in the
IIIA–IV stage GC plasma vs IA–IIA stage GC plasma among all the candidate mRNAs
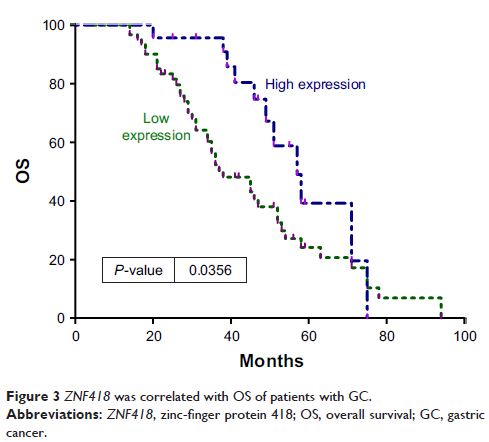
according to the Student’s t -test. Results showed that a decrease in the ZNF418 expression level was
associated with the presence of GC and also with higher tumor–node–metastasis
stage and lower OS rates compared with that in adjacent noncancerous tissues.
Cox regression analysis results demonstrated that the OS was independently
correlated with ZNF418 expression.
Finally, the prediction results showed that a total of eight mRNAs might have
an interaction with ZNF418 in both
STRING and GEPIA databases.
Conclusion: ZNF418 was first identified to be significantly downregulated in GC. Our study
indicated that ZNF418 might serve as a
novel biomarker for GC and was involved in GC development.
Keywords: plasma, diagnosis, prognosis, biomarker