111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

心房利钠肽修饰的油酸腺苷前体药物脂质纳米载体治疗心肌梗死的体外和体内评价
Authors Yu J, Li W, Yu D
Received 27 February 2018
Accepted for publication 10 April 2018
Published 11 June 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1697—1706
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S166749
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios Panos
Purpose: Myocardial
infarction is a major cause of mortality and heart failure worldwide. One of
the most effective methods of this injury is direct delivery of
cardioprotective drugs to ischemia–reperfusion (IR) myocardium. The aim of the
present study was to fabricate an adenosine (Ade) prodrug-based, atrial
natriuretic peptide (ANP)-modified nanosystem for the treatment of myocardial
infarction.
Materials and
methods: Oleate adenosine prodrug (Ade-OA)
and ANP-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol were
synthesized. ANP-modified Ade-loaded lipid nanocarriers (ANP Ade/LNCs) were
then self-assembled by using solvent evaporation method. In vitro drug release
in the presence of plasma was evaluated. In vivo inhibition effect on infarct
size, tissue distribution, and pharmacokinetics were investigated in rats with
ischemic myocardium after intravenous injection.
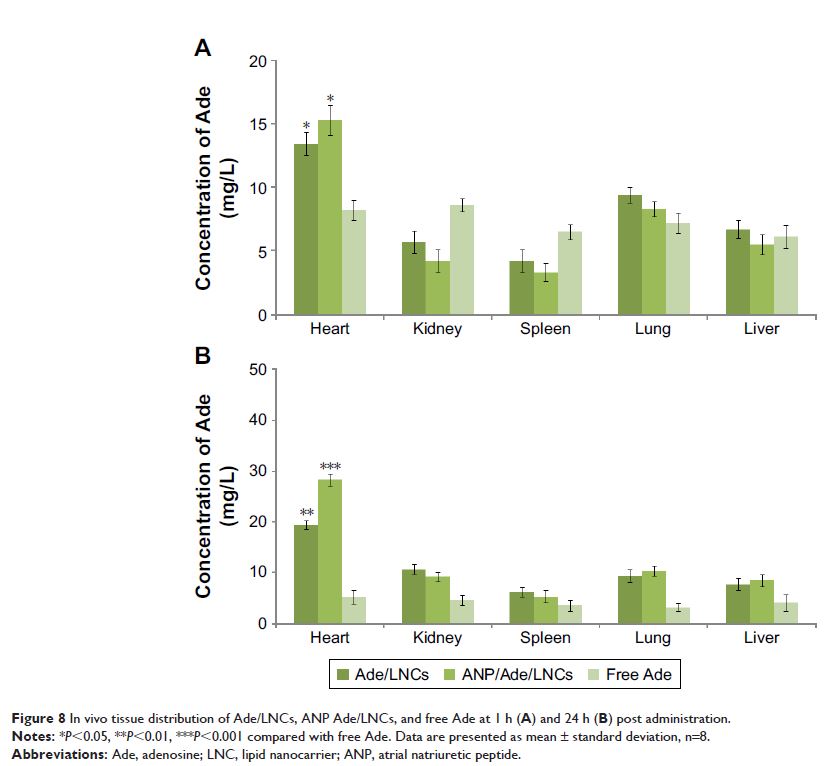
Results: In vivo inhibition effect on infarct size, tissue distribution,
and pharmacokinetics studies in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) rats showed
that ANP Ade/LNCs exhibited better efficiency than non-modified Ade/LNCs and
free Ade in all respects.
Conclusion: These results indicated that the ANP Ade/LNCs can be used as a
promising system for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: myocardial infarction, atrial natriuretic peptide, lipid
nanoparticles, adenosine, prodrug