111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国汉族人群 TERT 基因多态性与非小细胞肺癌易感性研究
Authors Li C, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang X, Sun M, Liu S, Sun L, Shi L, Yao Y
Received 22 February 2018
Accepted for publication 19 April 2018
Published 11 June 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1487—1495
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S166235
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Recent
studies have revealed that the TERT gene
plays crucial roles in cancer initiation and development. Genome-wide analysis
studies and case-control studies have demonstrated that polymorphisms in
the TERT gene are associated with
various cancers.
Materials and
methods: In the current study, we
analyzed the associations of eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in
the TERT gene with non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) in a Chinese Han population. A total of 467 NSCLC patients
and 526 healthy individuals were recruited for SNP genotyping using a TaqMan
assay.
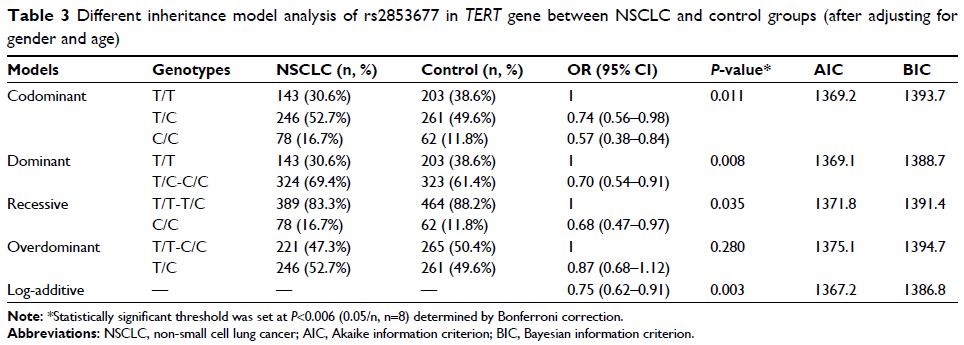
Results: Our results revealed that the allelic frequencies of rs2853677 and
rs2853691 were significantly different between the NSCLC and control groups (P =0.004 and 0.001, respectively).
Moreover, the T allele of rs2853677 and the A allele of rs2853691 might be the
protective factors against NSCLC (OR=0.766; 95%CI: 0.639–0.918 and OR=0.714;
95%CI: 0.584–0.875, respectively). Additionally, stratified association
analysis of the eight SNPs with the different pathological NSCLC stages (I+II
and III+IV) and different pathological types (adenocarcinoma and squamous cell
carcinoma) revealed that none of the SNPs were significantly different between
patients with different pathological stages and pathological types.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that rs2853677 and rs2853691 in the TERT gene might be associated
with NSCLC in this Chinese Han population.
Keywords: TERT gene, polymorphisms,
lung cancer, Chinese Han population