111536
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

五种血清生物标志物在肝细胞癌早期诊断中的直接比较
Authors Chen H, Zhang Y, Li S, Li N, Chen Y, Zhang B, Qu C, Ding H, Huang J, Dai M
Received 1 March 2018
Accepted for publication 17 April 2018
Published 10 July 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 1947—1958
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167036
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Although a number of serum biomarkers for detection of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have been explored, their exact diagnostic value
remains unclear. We aimed to conduct a direct comparison of five representative
serum biomarkers for detecting HCC and to derive multi-marker prediction
algorithms.
Patients and
methods: In total, 846 patients were
recruited from three hospitals in China, including 202 HCC patients, 226 liver cirrhosis
patients, 215 chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients, and 203 healthy
volunteers. Serum levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), lens culinaris
agglutinin-reactive AFP (AFP-L3), des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), squamous
cell carcinoma antigen, and centromere protein F autoantibody were measured by
ELISA. The diagnostic performances of individual biomarkers and multi-marker
combinations were evaluated by receiver operating characteristics analysis. The
bootstrapping method was adopted to adjust for potential overfitting of all
diagnostic indicators.
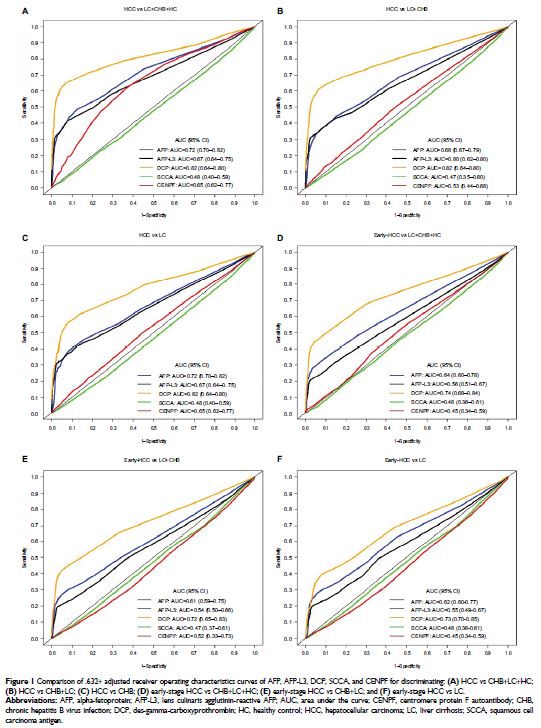
Results: DCP exhibited the best diagnostic performance, with areas under the
curve (AUC) for detecting HCC of 0.82 (95% CI 0.64–0.80) and sensitivity of
65.2% (95% CI 63.3–82.1%) at 90% specificity. Of note, DCP showed similar
diagnostic efficacy for detecting AFP-positive and AFP-negative HCC. After a
comprehensive search for multi-marker combinations, a two-marker prediction
algorithm including AFP and DCP was constructed and yielded an AUC of 0.87 (95%
CI 0.68–0.84) for detecting HCC. In addition, the combination showed good
ability in discriminating early-stage HCC and decompensated liver cirrhosis,
with an AUC of 0.81 (95% CI 0.75–0.86).
Conclusion: DCP could be a complementary biomarker in the early diagnosis of HCC.
The constructed multi-marker prediction algorithms could contribute toward
distinguishing HCC from non-malignant chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: early detection, liver cirrhosis, prediction model