108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

copine-III 表达的沉默增强了肝细胞癌细胞对分子靶向剂索拉非尼的敏感性
Authors Chen Z, Jiang ZK, Zhang WZ, He BX
Received 9 March 2018
Accepted for publication 15 May 2018
Published 29 August 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3057—3067
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167781
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
Background: The application of the oral targeted therapeutic agent sorafenib provides new hope for patients suffering from advanced stages of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the prognosis of such patients remains poor due to the rapid development of the multidrug resistance process in cancer pathogenesis. The present work evaluated whether copine-III, a novel cancer regulator encoded by the CPNE3 gene, would be a potential indicator of sorafenib resistance in HCC treatment.
Materials and methods: The endogenous expression of copine-III in clinical specimens was examined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Copine-III siRNA was transfected into HCC cells to downregulate copine-III expression. The effect of copine-III on sorafenib’s antitumor activation was identified by in vitro and in vivo experiments (MTT, Transwell, and flow cytometry as well as a nude mice model).
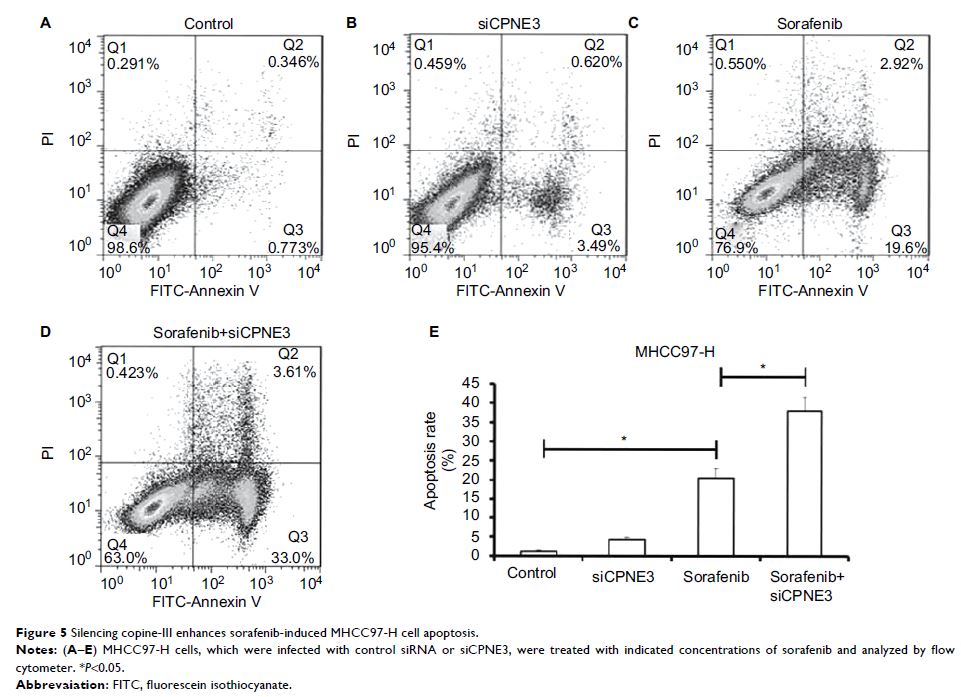
Results: High levels of copine-III in clinical specimens are related to poor prognosis of advanced HCC patients on sorafenib treatment. Infection of Ad-siCPNE3 significantly decreased the endogenous expression of copine-III and enhanced the susceptibility of MHCC97-H cells to sorafenib: the IC50 value decreased from 1.15±0.11 to 0.25±0.05 μmol/L. Moreover, silencing copine-III enhanced the effect of sorafenib on apoptosis, in vitro invasion/migration, and subcutaneous or intrahepatic growth of MHCC97-H cells in nude mice.
Conclusion: Copine-III is a novel potential indicator of prognosis for patients who received sorafenib for advanced HCC treatment.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, CPNE3, copine-III, molecular targeted agent, sorafenib-resistance