111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

黄芪甲苷/lncRNA-TUG1/TRAF5 信号通路会参与糖尿病肾病大鼠的足细胞凋亡
Authors Lei X, Zhang L, Li Z, Ren J
Received 24 February 2018
Accepted for publication 31 May 2018
Published 6 September 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 2785—2793
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S166525
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Objective: This study aims to figure out the mechanism of astragaloside IV (AS-IV) in the protection of podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy (DN) rats.
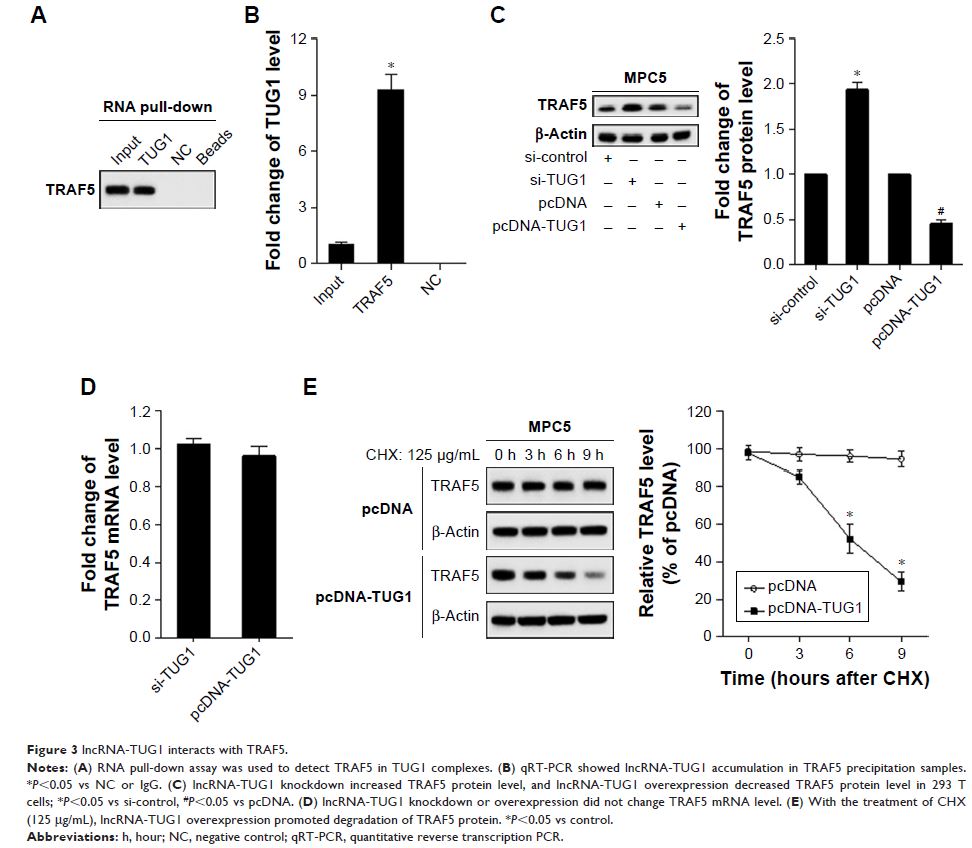
Materials and methods: Streptozotocin (STZ) was used to induce diabetes in rats, and the diabetic rats were treated with 5 mg/kg/d of AS-IV for 12 weeks. Albuminuria level, relative TUG1 and TRAF5 levels, and TRAF5 and cleaved-caspase-3 protein levels were examined by ELISA, quantitative reverse transcription (qRT)-PCR, and Western blot analyses, respectively. The interaction between TUG1 and TRAF5 was confirmed by RNA pull-down and RNA precipitation. TUNEL assay was used to detect podocyte apoptosis.
Results: Compared with control rats, DN rats had higher albuminuria and TRAF5 levels and lower TUG1 level. AS-IV treatment attenuated albuminuria and TRAF5 levels and improved TUG1 level in DN rats. TUG1 was downregulated and TRAF5 was upregulated in high-glucose-treated MPC5 cells, and AS-IV ameliorated the TUG1 level. In addition, TUG1 interacted with TRAF5, and TUG1 overexpression promoted degradation of TRAF5 protein. Besides, AS-IV modulated TRAF5 expression through regulating TUG1. AS-IV decreased podocyte apoptosis via the TUG1/TRAF5 pathway. Finally, in vivo experiment proved that si-TUG1 abrogated the protective effect of AS-IV on DN.
Conclusion: AS-IV attenuated podocyte apoptosis and protected diabetic rats from DN via the lncRNA-TUG1/TRAF5 pathway.
Keywords: astragaloside IV, diabetic nephropathy, TUG1, TRAF5, albuminuria