111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

五次重复坐姿试验与 30 秒坐姿试验评估 COPD 患者运动耐量的比较研究
Authors Zhang Q, Li YX, Li XL, Yin Y, Li RL, Qiao X, Li W, Ma HF, Ma WH, Han YF, Zeng GQ, Wang QY, Kang J, Hou G
Received 8 May 2018
Accepted for publication 25 July 2018
Published 10 September 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2833—2839
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S173509
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Chunxue Bai
Purpose: The sit-to-stand test (STST) has been used to evaluate the exercise tolerance of patients with COPD. However, mutual comparisons to predict poor exercise tolerance have been hindered by the variety of STST modes used in previous studies, which also did not consider patients’ subjective perceptions of different STST modes. Our aim was to compare the five-repetition sit-to-stand test (5STS) with the 30-second sit-to-stand test (30STS) for predicting poor performance in the six-minute walking test and to evaluate patients’ subjective perceptions to determine the optimal mode for clinical practice.
Patients and methods: Patients with stable COPD performed 5STS, 30STS and the 6MWT and then evaluated their feelings about the two STST modes by Borg dyspnea score and a questionnaire. Moreover, we collected data through the pulmonary function test, mMRC dyspnea score, COPD assessment test and quadriceps muscle strength (QMS). A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of the 5STS and 30STS results was used to predict 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) <350 m.
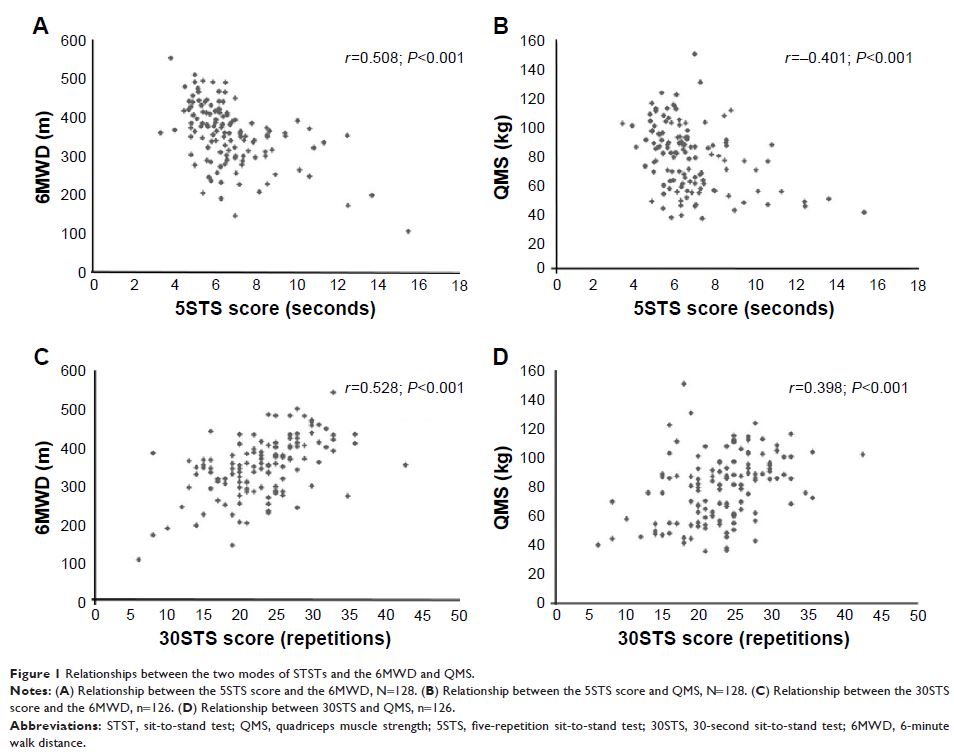
Results: The final analysis included 128 patients. Similar moderate correlations were observed between 6MWT and 5STS (r =-0.508, P <0.001) and between 6MWT and 30STS (r =0.528, P <0.001), and there were similar correlations between QMS and 5STS (r =-0.401, P <0.001) and between QMS and 30STS (r =0.398, P <0.001). The 5STS and 30STS score cutoffs produced sensitivity, specificity and positive and negative predictive values of 76.0%, 62.8%, 56.7% and 80.3% (5STS) and 62.0%, 75.0%, 62.0% and 75.0% (30STS), respectively, for predicting poor 6MWT performance. The 5STS exhibited obvious superiority in terms of the completion rate and the subjective feelings of the participants.
Conclusion: As a primary screening test for predicting poor 6MWD, the 5STS is similar to the 30STS in terms of sensitivity and specificity, but the 5STS has a better patient experience.
Keywords: sit-to-stand test, six-minute walk test, COPD, exercise endurance