111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

EGFR 和 KRAS 对切除术治疗的非小细胞肺癌的预后价值:系统综述和荟萃分析
Authors Zhang SM, Zhu QG, Ding XX, Lin S, Zhao J, Guan L, Li T, He B, Zhang HQ
Received 7 March 2018
Accepted for publication 10 May 2018
Published 10 September 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 3393—3404
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167578
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leylah Drusbosky
Background: The prognostic value of EGFR and KRAS mutations in resected non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been reported. However, conflicting results were reported in these studies. The effect of mutations in these two genes in resected NSCLC remains controversial.
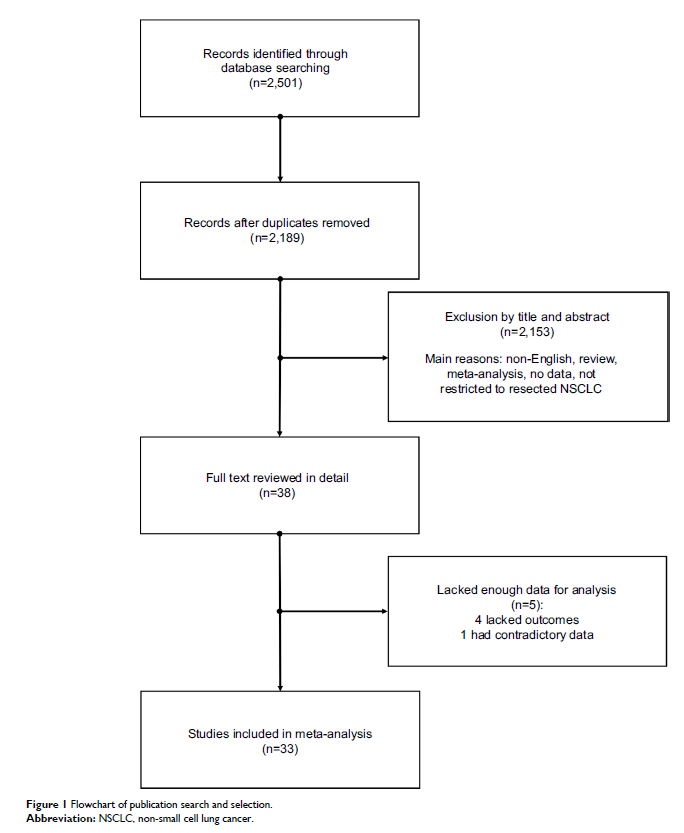
Methods: We searched Internet databases for studies reporting disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in resected NSCLC patients with EGFR or KRAS mutations. A meta-analysis calculating the pooled hazard ratio (HR) for DFS and OS was used to measure the association of EGFR or KRAS mutations with the prognosis of patients after surgery.
Results: A total of 9,635 patients from 32 studies were included in this analysis. The combined HR for EGFR mutations on DFS was 0.77 (95% CI 0.66–0.90, p =0.001) and on OS was 0.72 (95% CI 0.66–0.80, p <0.00001). In addition, the combined HR for KRAS mutations on DFS was 1.5 (95% CI 1.15–1.96, p =0.002) and on OS was 1.49 (95% CI 1.28–1.73, p <0.00001). Sensitivity analysis, subgroup analysis, and bias analysis proved the stability of the results.
Conclusion: The analysis showed that EGFR mutations were significantly associated with DFS and OS. These findings indicated that surgically treated NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations were inclined to exhibit a prolonged DFS and OS. In addition, the results indicated that KRAS mutations predicted worse DFS and OS in patients with resected NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR mutations, KRAS mutations, meta-analysis, non-small cell lung cancer, prognosis, resected