111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

亚洲人群中 microRNAs 多态性与缺血性卒中的关系:基于 6,083 个病例和 7,248 例对照研究的证据
Authors Zou DH, Liu CB, Zhang Q, Li XF, Qin G, Huang Q, Meng YS, Chen L, Wei JR
Received 13 May 2018
Accepted for publication 14 July 2018
Published 12 September 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 1709—1726
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S174000
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Wu
Background: Polymorphisms in miR-146a (rs2910164), miR-196a2 (rs11614913), miR-149 (rs2292832) and miR-499 (rs3746444) have been associated with ischemic stroke (IS), but studies have given inconsistent results.
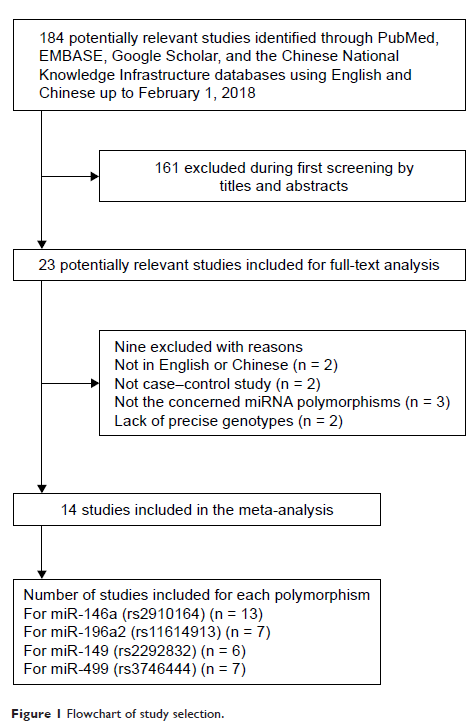
Methods: This meta-analysis investigated the possible association between IS risk and the four polymorphisms. A total of 14 case-control studies from Asian populations involving 6,083 cases and 7,248 controls for the four polymorphisms were included.
Results: Results showed that the GG genotype of miR-146a (rs2910164) may be associated with increased IS risk according to the recessive model (OR=1.20, 95% CI=1.02-1.42, P =0.03). Similarly, the CC genotype of miR-149 (rs2292832) may be associated with increased IS risk according to the recessive model (OR=1.28, 95% CI=1.08-1.52, P =0.005) and the homozygous model (OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.09-1.58, P =0.004). In contrast, miR-196a2 (rs11614913) and miR-499 (rs3746444) polymorphisms did not show significant association with IS risk in any of the five genetic models.
Conclusion: These results indicate that the GG genotype of miR-146a (rs2910164) and CC genotype of miR-149 (rs2292832) may confer increased susceptibility to IS, while miR-196a2 (rs11614913) and miR-499 (rs3746444) polymorphisms may not be associated with IS risk in Asian populations. These conclusions should be verified in large and well-designed studies.
Keywords: miRNAs, polymorphism, ischemic stroke, meta-analysis