111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA LINC00882 的过表达与肝细胞癌的预后不良有关
Authors Zhu L, Huang F, Wan T, Xu H, Zhao Q
Received 11 April 2018
Accepted for publication 17 May 2018
Published 13 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5209—5217
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S170825
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third major cause of malignant tumor-related death worldwide because it is initially diagnosed in the advanced stage and its therapeutic outcomes are usually poor. Based on this, it is urgent to identify effective early diagnosis biomarkers and new therapeutic targets to promote HCC treatment. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been reported as promising biomarkers for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Materials and methods: In this study, we profiled expression patterns and dysregulation of lncRNAs in HCC tissues by analyzing two datasets GSE55191 and GSE64631 from Gene Expression Omnibus database firstly, each of which contains expression profiles of 3 primary HCC tissues and 3 normal liver tissues, respectively.
Results: LncRNA 882 (LINC00882) is one of the lncRNAs that was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues compared with normal liver tissues. We verified the upregulation of LINC00882 in HCC by using two separate cohorts that contained 85 HCC tissues and paired adjacent noncancerous tissues and 86 HCC tissues and 89 independent noncancerous liver tissues, respectively.
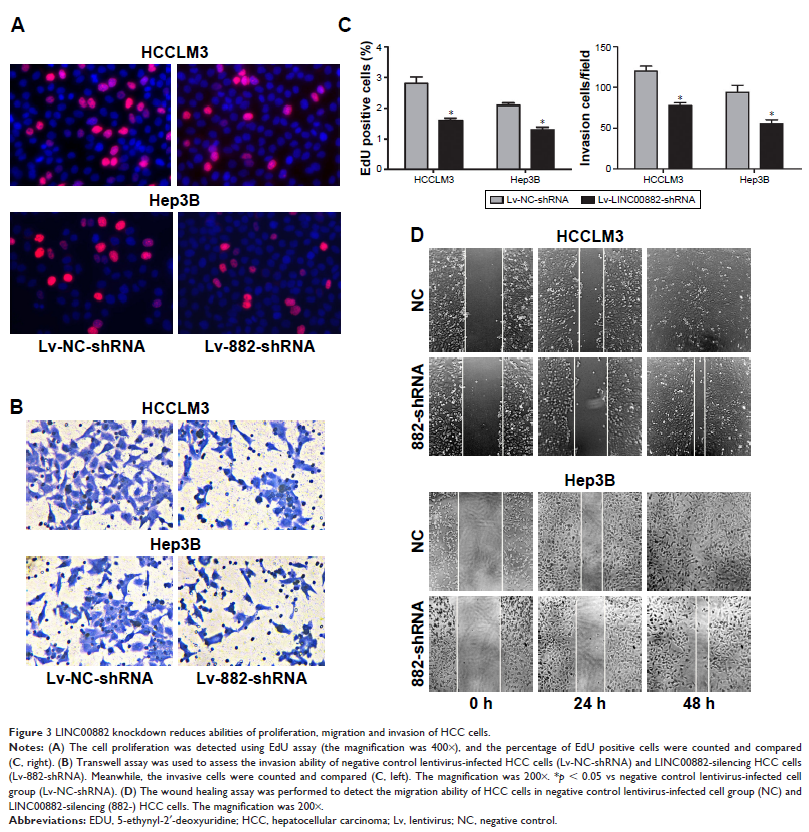
Discussion: We found that upregulation of LINC00882 is correlated with poorer prognosis of HCC patients. In vitro cell experiments demonstrated that knockdown of LINC00882 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cell lines.
Conclusion: These results indicated that LINC00882 promotes HCC progression and could be a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, long noncoding RNAs, LINC00882, proliferation, migration