111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

建立一种新型的基于均相纳米粒子的实验技术,用于对超低容量血清样品进行敏感性降钙素原检测
Authors Li P, Chen Z, Liu B, Li K, Wang H, Lin L, He L, Wei J, Liu T
Received 17 May 2018
Accepted for publication 4 July 2018
Published 13 September 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 5395—5404
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S173776
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: Sepsis is a potentially fatal systemic body infection with a significant mortality rate worldwide. Although C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and procalcitonin (PCT) might be biomarkers for sepsis diagnosis, PCT is more sensitive and specific than CRP or IL-6. We aimed to establish an efficient immunoassay that precisely detects PCT in human serum for the early diagnosis of sepsis.
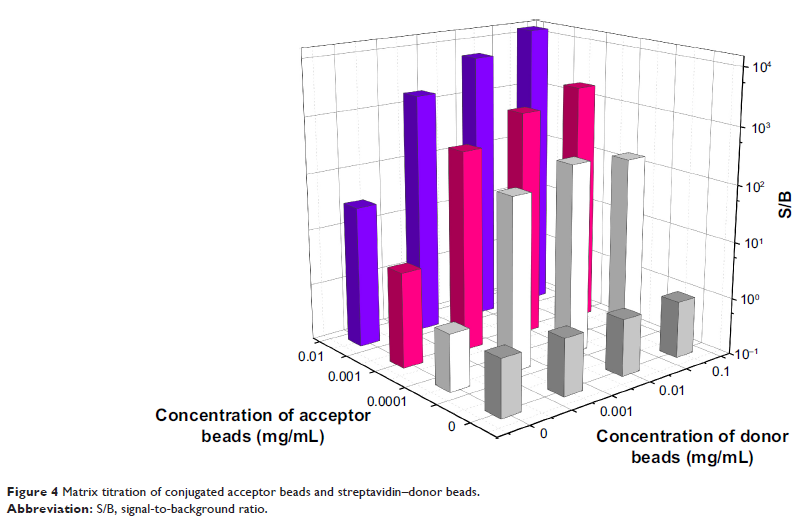
Materials and methods: We developed a novel amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay (AlphaLISA) for the quantitative detection of PCT in serum. In this assay, a pair of antibodies was used to capture PCT in serum and to form sandwich complexes after incubating for 15 minutes at 37°C.
Results: PCT concentrations were determined within a linear range of 0.016–100 ng/mL. The limit of detection was 18.6 pg/mL. The results demonstrate that the reproducibility, recovery, and specificity of this assay for PCT meet the requirements of clinical detection. The coefficient of determination (R 2) between this method and commercially available enzyme-linked fluorescent assay (ELFA) kits was estimated to be 0.93045 in clinical serum testing.
Conclusion: The novel assay for PCT detection was robust with high sensitivity and a broad dynamic range. Compared with conventional heterogeneous detection methods such as ELISA, this assay measured the concentration of the homogeneous form of PCT and provided results that are more accurate within a shorter detection time. We expect that this novel method will be useful for the early screening and prognosis evaluation of patients with sepsis.
Keywords: sepsis, procalcitonin, nanoparticles, quantitative detection, homogeneous immunoassay