111446
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在没有慢性肾病的中国社区人群中,不同葡萄糖性状与肾功能的关联降低了风险
Authors Wang X, Fan F, Jia J, Xu X, Qin X, Zheng B, Li H, Dong L, Wang S, Li J, Huo Y, Dou J, Zhang Y
Received 4 March 2018
Accepted for publication 21 June 2018
Published 17 September 2018 Volume 2018:14 Pages 1725—1734
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S167233
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has become a major issue worldwide
and hyperglycemia is known as an important risk factor responsible for CKD
progression. Few studies have investigated whether fasting plasma glucose (FPG)
could predict kidney function decline (KFD) risk better than postprandial
plasma glucose, and vice versa. In this study, we investigated the roles of FPG
and 2-hour plasma glucose (2 h-PG) in predicting KFD risk in a Chinese
community-based population without baseline deterioration of kidney functions.
Methods: Subjects with normal kidney function from an atherosclerosis
cohort in Beijing, China were followed up for 2.3 years. The outcome was KFD (a
drop in glomerular filtration rate category accompanied by 25% or greater
decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate from the baseline or a
sustained decline of more than 5 mL/min/1.73 m2/year rate).
Results: A total of 3,738 subjects were included of which, 7.7% of the
subjects suffered from KFD. After covariates adjustments, both FPG (OR
=1.23, P <0.001) and 2 h-PG (OR
=1.07, P <0.001) were associated with
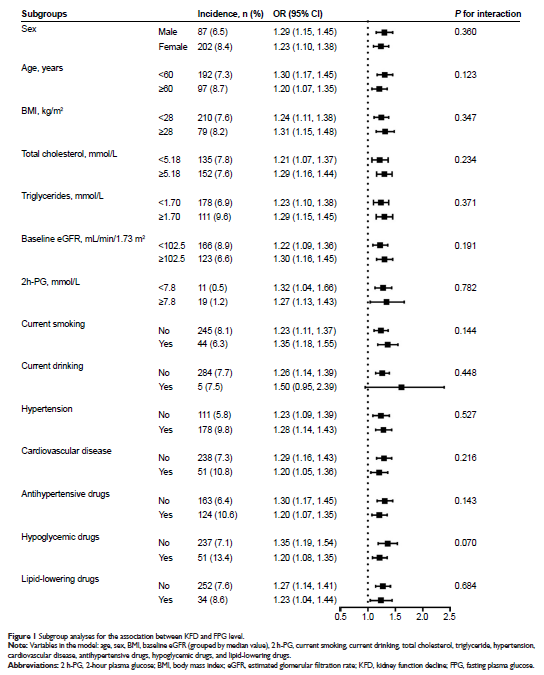
KFD. Furthermore, FPG was independent of 2 h-PG to predict KFD (OR =1.26, P <0.001). Subgroup analyses and
interaction tests including diabetes mellitus, after adjusting all covariates,
revealed no significant heterogeneity among analyzed subgroups. We also found
subjects with FPG level of 6.1–7.0 mmol/L and >7.0 mmol/L had 1.83 times and
2.51 times KFD risk respectively, compared to subjects with FPG level <5.6
mmol/L.
Conclusion: FPG was superior to 2 h-PG in predicting KFD in a Chinese
community-based population without CKD. FPG screening may be an important measure
for CKD primary prevention even in subjects with impaired fasting glucose.
Keywords: fasting plasma glucose, postprandial plasma glucose, kidney
function decline, chronic kidney disease