111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

脂蛋白(a): 治愈性切除术后肝细胞癌患者的一个有前途的预后生物标志物
Authors Gao XH, Zhang SS, Chen H, Wang K, Xie W, Wang F
Received 1 February 2018
Accepted for publication 2 July 2018
Published 17 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 5917—5924
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164273
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: This study aimed to explore serum lipoprotein (a) (Lp(a)) levels
and investigate their prognostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
patients after curative resection.
Materials and
methods: One cohort of 102 healthy
individuals, one cohort of 172 HCC patients, and one cohort of 171 HCC patients
undergoing curative resection were studied to evaluate serum Lp(a) levels and
their prognostic significance, using Kaplan–Meier curves and log-rank tests.
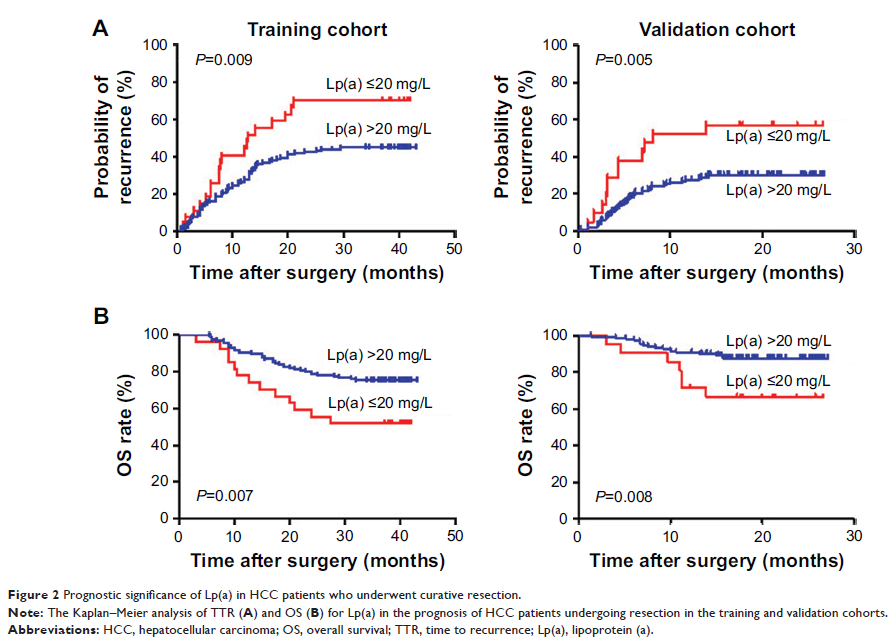
Results: The Lp(a) levels in HCC patients were significantly lower than
those in healthy individuals. Furthermore, the levels in HCC patients were
significantly associated with recurrence. HCC patients were stratified into
high Lp(a) (>20 mg/L) and low Lp(a) (≤20 mg/L) groups, using an optimal
cutoff point for the Lp(a) of 20 mg/L. Low Lp(a) levels significantly
correlated with tumor recurrence and survival time; HCC patients with low Lp(a)
levels had higher recurrence rates and shorter survival time than those with
high Lp(a) levels; Lp(a) was an independent prognostic factor for relapse-free
survival and overall survival, and retained its prognostic value for
α-fetoprotein ≤400 ng/mL and tumor size ≤5 cm subgroups in the training and
validation cohorts.
Conclusion: Lp(a) was a promising and useful marker for assessing and
monitoring recurrence and prognosis of patients with HCC, and improving Lp(a)
levels may be a promising therapeutic strategy in HCC patients.
Keywords: lipoprotein (a), hepatocellular carcinoma, recurrence, prognosis,
survival, LP(a), HCC, recurrence, biomarker