111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

经直肠超声引导的前列腺穿刺活检后感染并发症的危险因素
Authors Wu YP, Li XD, Ke ZB, Chen SH, Chen PZ, Wei Y, Huang JB, Sun XL, Xue XY, Zheng QS, Xu N
Received 14 April 2018
Accepted for publication 6 June 2018
Published 17 September 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1491—1497
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S171162
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
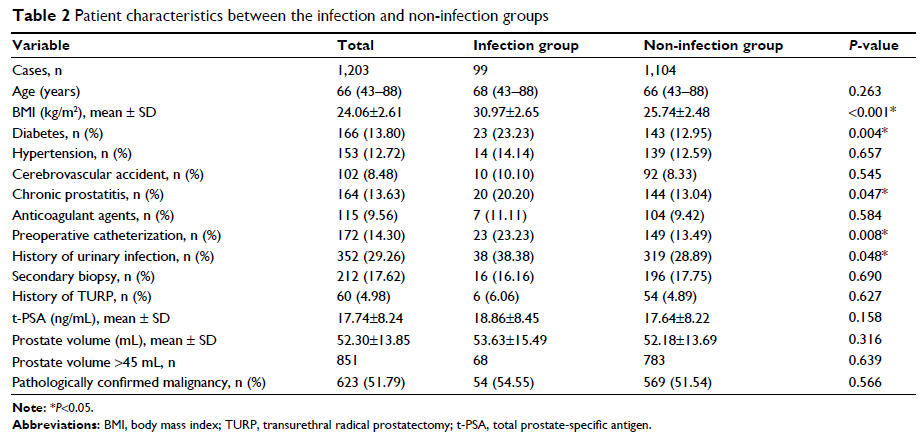
Objective: To explore risk factors of infectious complications following
transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy (TRUSPB).
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 1,203 patients with suspected prostate
cancer who underwent TRUSPB at our center between December 2012 and December
2016. Demographics, clinical characteristics, and data regarding complications
were collected, and then univariate and multivariate logistic regression
analyses were used to identify independent risk factors for infectious
complications after prostate biopsy.
Results: Multivariate logistic analysis demonstrated that body mass index
(BMI) (OR=2.339, 95% CI 2.029–2.697, P <0.001),
history of diabetes (OR=2.203, 95% CI 1.090–4.455, P =0.028), and preoperative
catheterization (OR=2.303, 95% CI 1.119–4.737, P =0.023)
were risk factors for infection after prostate biopsy. The area under the
receiver operating characteristics curve for infectious complications was 0.930
(95% CI 0.907–0.953, P <0.001).
BMI=28.196 kg/m2 was the best
cut-off threshold for predicting infection after TRUSPB.
Conclusion: BMI >28.196 kg/m2, history of diabetes, and preoperative catheterization are independent
risk factors for infection after prostate biopsy.
Keywords: body mass index, diabetes mellitus, preoperative catheterization,
infectious complications, transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy