111314
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SPHK1 在慢病毒介导下的 siRNA 敲除可抑制神经母细胞瘤的增殖和肿瘤发生
Authors Su L, Tian J, Sun J, Han N, Feng L, Yu B, Wang Y
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 19 September 2018
Published 18 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7187—7196
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S180962
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Background: The overexpression of sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) is responsible
for the progress of many cancers. However, the role of SPHK1 in the development
and progression of neuroblastoma (NB) remain largely unknown. Here in this
study, we explored whether silencing SPHK1 by lentivirus-mediated siRNA could
be employed as a potential therapeutic target for NB.
Materials and
methods: Lentivirus was adopted to load
SPHK1 siRNA. The results were obtained using RT-qPCR, Western blot, cell
proliferation assay, transwell cell migration/invasion assays as well as in
vivo xenograft tumor models in nude mice.
Results: Our results demonstrated that SPHK1 mRNA was upregulated in SH-SY5Y and
SK-N-SH cells as well as in human NB tissues. SPHK1 knockdown by siRNA resulted
in impaired proliferation, increased apoptosis, as well as impaired migration
and invasion of SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. In addition, the in vivo study
suggested that SPHK1 knockdown significantly reduced the tumorigenesis of
SH-SY5Y xenograft model. Furthermore, intratumorally administered
lentivirus-SPHK1 siRNA could significantly inhibit tumor growth in an SH-SY5Y
xenograft mice model. Intensive investigations on mechanism revealed that these
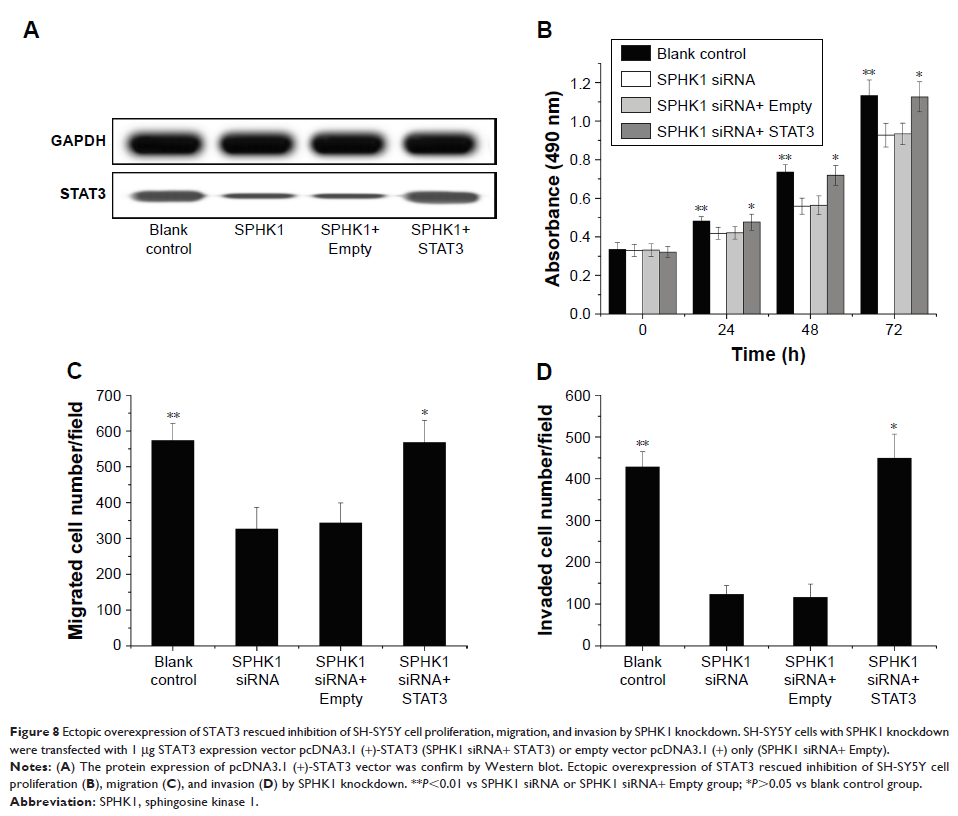
effects were achieved through the deactivation of STAT3 pathways.
Conclusion: These data suggest that SPHK1 inhibition via downregulation of
STAT3 pathways by lentivirus-mediated siRNA knockdown can significantly
suppress NB progression, which could be a promising target for future gene
therapy of NB.
Keywords: lentivirus, siRNA, SPHK1, STAT3, neuroblastoma