110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

电针可增强膝关节骨性关节炎小鼠模型中外周 CB2 受体对慢性疼痛的抑制作用
Authors Yuan X, Wang Q, Su W, Li HP, Wu CH, Gao F, Xiang HC, Zhu H, Lin LX, Hu XF, Cao J, Li JJ, Li M
Received 19 April 2018
Accepted for publication 10 August 2018
Published 8 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2797—2808
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S171664
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Minal Joshi
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Purpose: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a highly prevalent, chronic joint
disorder, with chronic pain as its typical symptom. Although studies have shown
that an activated peripheral CB2 receptor can reduce acute pain, whether the
CB2 receptor is involved in electroacupuncture (EA) inhibiting chronic pain and
the involved mechanism remains unclear. The aim of this study was to
investigate whether EA may strengthen peripheral CB2 receptor-inhibited chronic
pain in a mouse model of KOA.
Materials and
methods: KOA was induced by intra-articular
injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) into the left knee joint of mice.
Thermal hyperalgesia was tested with the hot plate test, and mechanical
allodynia was quantified using von Frey filaments. The expression of CB2
receptor and IL-1β were quantified by using immunofluorescence labeling.
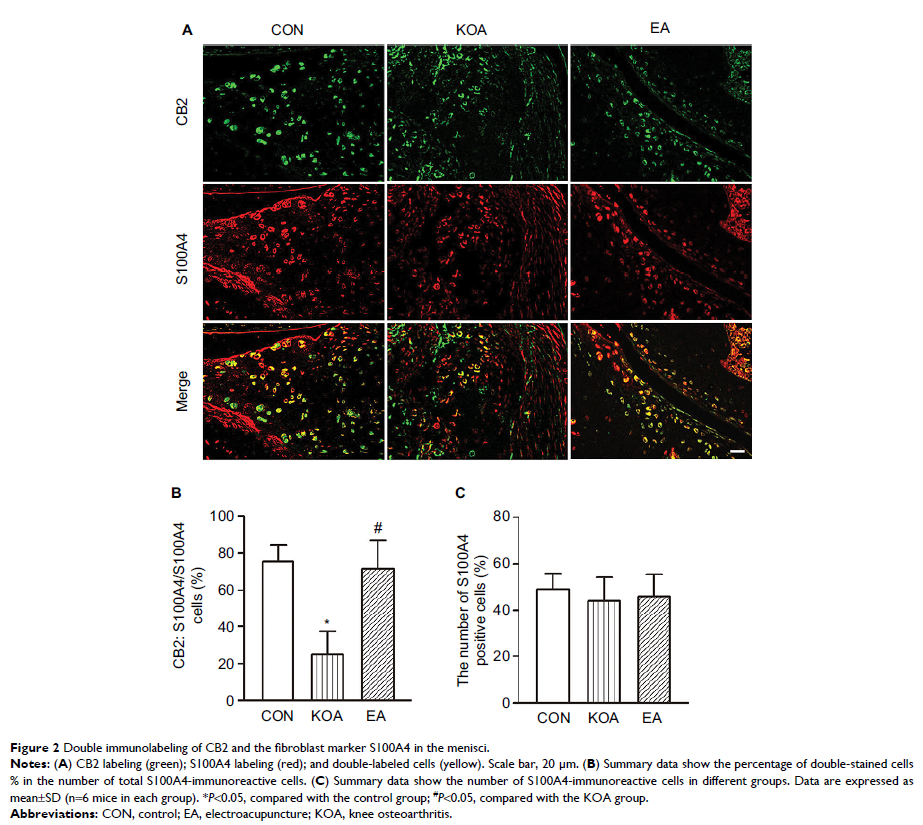
Results: EA treatment at 2 Hz+1 mA significantly increased the
expression of CB2 receptor in fibroblasts and decreased the expression of IL-1β
in the menisci compared with that in the KOA group. However, EA had no effect
on the expression of IL-1β in CB2−/− mice. At 2 Hz+1 mA, EA significantly increased
mechanical threshold, thermal latency, and weight borne after KOA modeling.
However, knockout of the CB2 receptor blocked these effects of EA. After
2 Hz+1 mA treatment, EA significantly reduced the Osteoarthritis
Research Society International (OARSI) score after KOA modeling. However, EA
had no significant effect on the OARSI score in CB2−/− mice.
Conclusion: EA reduced the expression of IL-1β by activating the CB2 receptor, thus
inhibiting the chronic pain in the mouse model of KOA.
Keywords: cannabinoid, acupuncture, inflammatory pain, IL-1β