110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文已被撤回 - 确定与卵巢透明细胞癌相关的潜在关键基因
Authors Xu Y, Shen K
Received 11 September 2018
Accepted for publication 12 October 2018
Published 8 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5461—5470
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187156
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
应作者的要求,癌症管理与研究期刊的主编决定撤回此文章。
撤稿启事
Background: Ovarian cancer is the major cause of death from cancer among
females worldwide. Ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) is considered a distinct
histopathologic subtype with worse prognosis and resistance to conventional
chemotherapy.
Materials and
methods: We analyzed five microarray datasets
derived from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. GEO2R tool was used to
screen out differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between OCCC tumor and normal
ovary tissue. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway
enrichment analysis were performed using the g:Profiler database and Cytoscape.
Based on Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes, we performed
protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis on the DEGs. Real-time PCR
(RT-PCR) and Western blotting in frozen samples of normal ovary and OCCC were
performed to verify the expression difference of hub genes in OCCC patients.
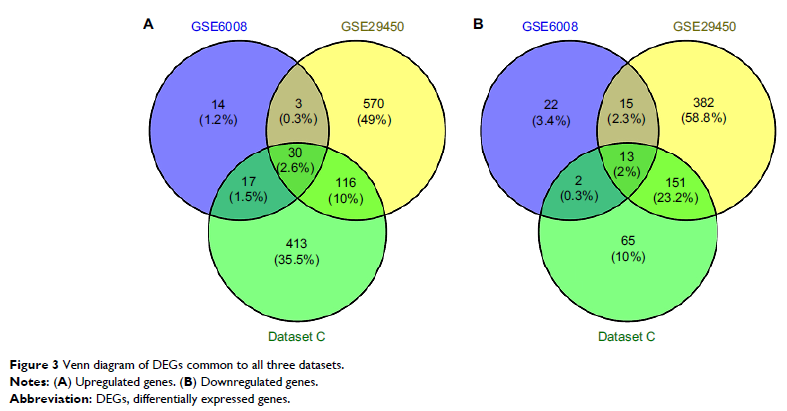
Results: Thirty upregulated DEGs and 13 downregulated DEGs were identified
by cross referencing. Six were chosen as hub genes with high connectivity
degree via PPI network analysis, including two upregulated and four
downregulated. RT-PCR and Western blotting results showed significant
expression difference of the two upregulated genes, SPP1 and EPCAM , between tumor and normal
tissues.
Conclusion: Our research suggests that SPP1 and EPCAM are overexpressed in
OCCC compared with normal ovary tissue. Clinical study of large sample is
required to evaluate the value of SPP1 and EPCAM in the precision
treatment and prognostic influence on OCCC in the future.
Keywords: ovarian clear cell carcinoma, differentially expressed
genes, SPP1 , EPCAM