110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

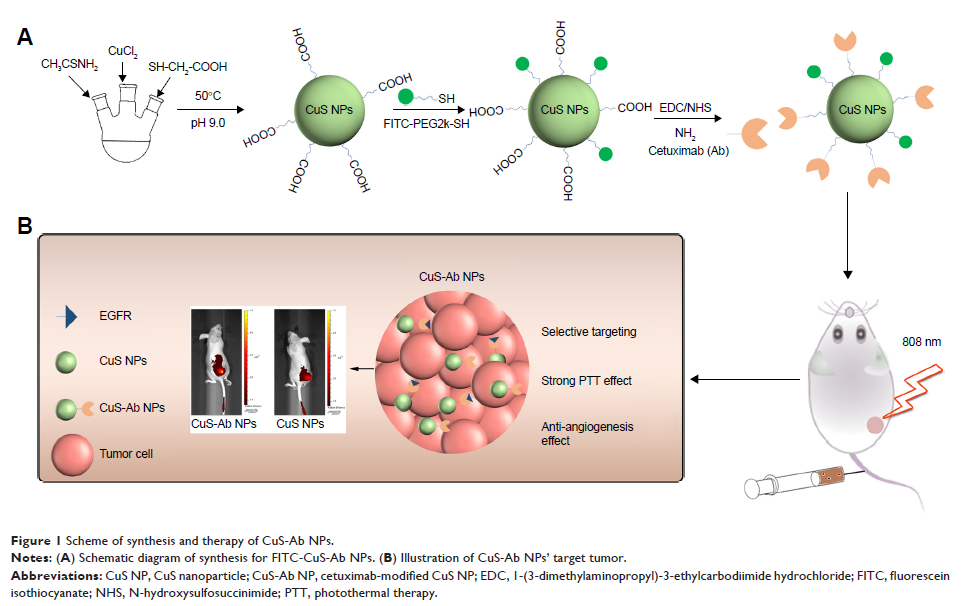
西妥昔单抗修饰的 CuS 纳米粒子用于近红外 II 响应光热疗法和抗血管治疗的整合
Authors Li B, Jiang Z, Xie D, Wang Y, Lao X
Received 17 July 2018
Accepted for publication 1 October 2018
Published 8 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7289—7302
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S175334
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Photothermal therapy (PTT) has received extensive attention owing
to its non-invasive nature and highly therapeutic outcomes. PTT agents and
near-infrared (NIR) laser are essential elements in PTT. However, most PTT
agents are composed of heavy metals, characterized by serious cytotoxicity and
side effects, and NIR irradiation often damages normal tissue owing to the high
dose, thus limiting the clinical application of PTT.
Purpose: In this regard, exploring new perspectives enabling more PTT
agents to be enriched into the tumor and NIR laser irradiation decay in PTT is
vital.
Methods: In this study, cetuximab (Ab), an anti-angiogenic antibody which
targets the EGFR, was modified on CuS NPs (CuS-Ab NPs) to improve the
aggregation of CuS NPs in the tumor.
Results: The cellular uptake data and the biodistribution results showed
comparable accumulation of CuS-Ab NPs in tumor, thus decreasing the
cytotoxicity and side effects in normal tissues. More importantly, the
modification of Ab in CuS-Ab NPs impressively inhibited the formation and
progression of tumor vessels, as demonstrated by immunohistochemistry staining.
The introduction of anti-vessel treatment requires CuS-Ab NPs to provide weak
PTT, which means that a small amount of laser energy is required, inevitably
causing negligible damage to normal tissue.
Conclusion: Therefore, our tailor-made CuS-Ab NPs have promising potential in
clinical applications.
Keywords: photothermal therapy, CuS NPs, active targeting, cetuximab, EGFR,
anti-angiogenesis