110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用 Wnt 信号通路和 EMT 过程实现长非编码 RNA H19 介导下的乳腺癌细胞化学敏感性
Authors Gao H, Hao G, Sun Y, Li L, Wang Y
Received 26 April 2018
Accepted for publication 9 August 2018
Published 9 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8001—8012
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S172379
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: Breast cancer is still one of the major public health burdens
worldwide, although there is tremendous progress in early diagnosis and
treatment of breast cancer. Tamoxifen was one of the most popular endocrine
therapies for early-stage estrogen receptor (ER) + breast cancer patients.
However, a high incidence of drug resistance develops along with poor prognosis
in breast cancer. Currently, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging and are
well suited to play a role in the development of cancer and tamoxifen
resistance. However, there is little reported about the relationship of breast
cancer resistance to tamoxifen and lncRNA H19. Here, we validated that lncRNA
H19 was highly expressed in breast cancer especially in patients with late
stage (III and IV), compared to normal tissues and early stage cancers (I and
II).
Methods: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was utilized for
comparison of lncRNA H19 expression level in breast cancers with different
stages. qPCR and Western blotting were used to detect gene and protein,
respectively.
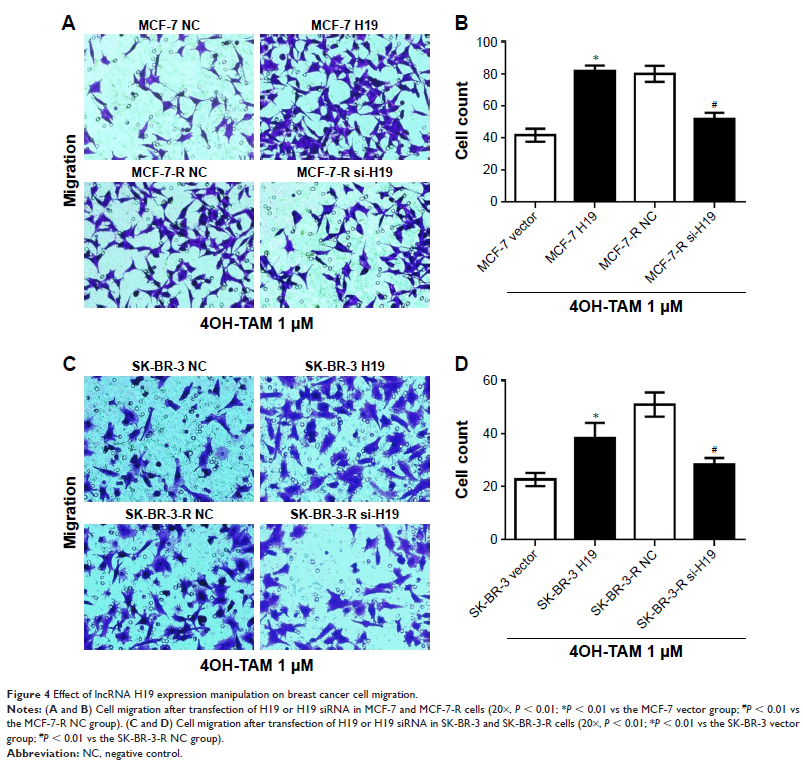
Results: We found that lncRNA H19 expression level manipulated breast
cancer cell proliferation both in parental breast cancer cell lines and
tamoxifen-resistant cell lines. Knockdown of lncRNA H19 elevated tamoxifen
sensitivity for promoting cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in tamoxifen-resistant
breast cancer cells. Moreover, knockdown of H19 inhibited Wnt pathway and
epithelia–mesenchymal transition in tamoxifen-resistance breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, the results of this study provided the evidence
for H19 in regulating tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and might provide novel
options in the future treatment of tamoxifen-resistance breast cancer patients.
Keywords: lncRNA H19, breast cancer, tamoxifen-resistance, EMT, Wnt pathway