110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-185 通过抑制 PI3K/AKT 和 Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路来遏制尤文氏肉瘤的发展
Authors Zhang S, Li D, Jiao G, Wang H, Yan T
Received 9 March 2018
Accepted for publication 19 August 2018
Published 9 November 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 7967—7977
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S167771
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Background: miRNAs are confirmed to play essential roles in tumorigenesis and
progression of cancers, including Ewing’s sarcoma. miR-185 has been reported to
be downregulated in some tumors, whereas the role of miR-185 in Ewing’s sarcoma
remains unclear.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to investigate the role of miR-185 in
the progression and metastasis of Ewing’s sarcoma and explore the associated
mechanism.
Materials and
methods: Ewing’s sarcoma cell line RD-ES was
transfected with pCMV-MIR-miR185 vector to upregulate the expression of
miR-185. Cell Counting Kit 8 and colony formation assays were used to assess
the effect of miR-185 on cell proliferation. The effect of miR-185 on cell
migration and invasion was detected by transwell assay. Flow cytometry assay
was performed to detect apoptosis rate of RD-ES cells. The protein levels of
apoptosis-related proteins was determined using Western blot assay or
immunohistochemistry assay. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to validate
the regulation between miR-185 and its target gene.
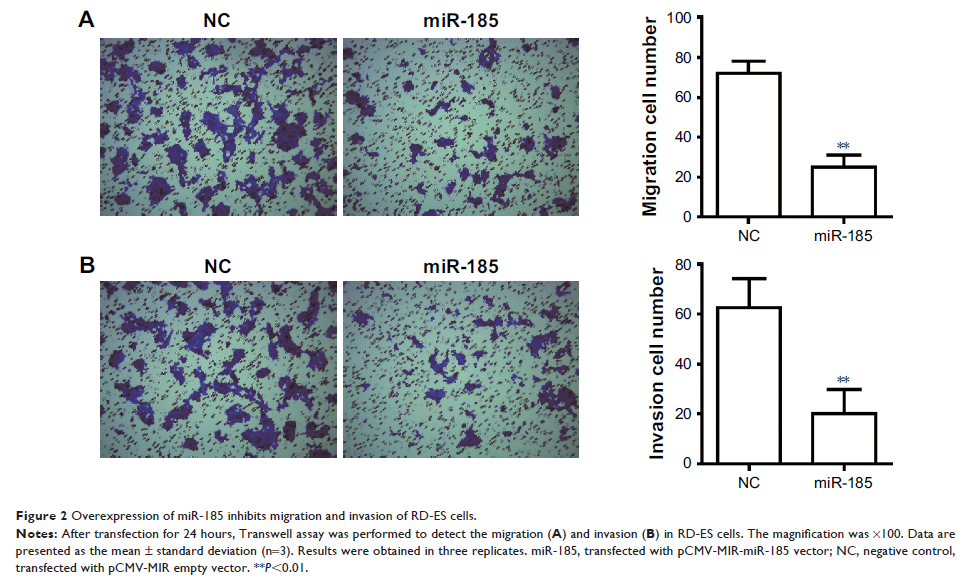
Results: Upregulation of miR-185 caused significant inhibition on cell
growth capacity, migration and invasion of Ewing’s sarcoma cell RD-ES. Besides,
upregulation of miR-185 was observed to accelerate cell apoptosis in a
mitochondrial pathway through regulating Bcl-2/Bax, Caspase 3, and Caspase 9 in
Ewing’s sarcoma in vitro . Moreover,
upregulation of miR-185 was found to suppress the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and
Wnt/β-catenin pathways in RD-ES cells. Furthermore, we identified that E2F6 was
a target gene for miR-185, and the suppression on cell proliferation caused by
overexpression of miR-185 was significantly rescued by the upregulation of E2F6
in RD-ES cells.
Conclusion: miR-185 is involved in cell growth, motility and survival of
Ewing’s sarcoma as a tumor suppressor via suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR and
Wnt/β-catenin pathways and targeting E2F6.
Keywords: miR-185, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, E2F6,
Ewing’s sarcoma